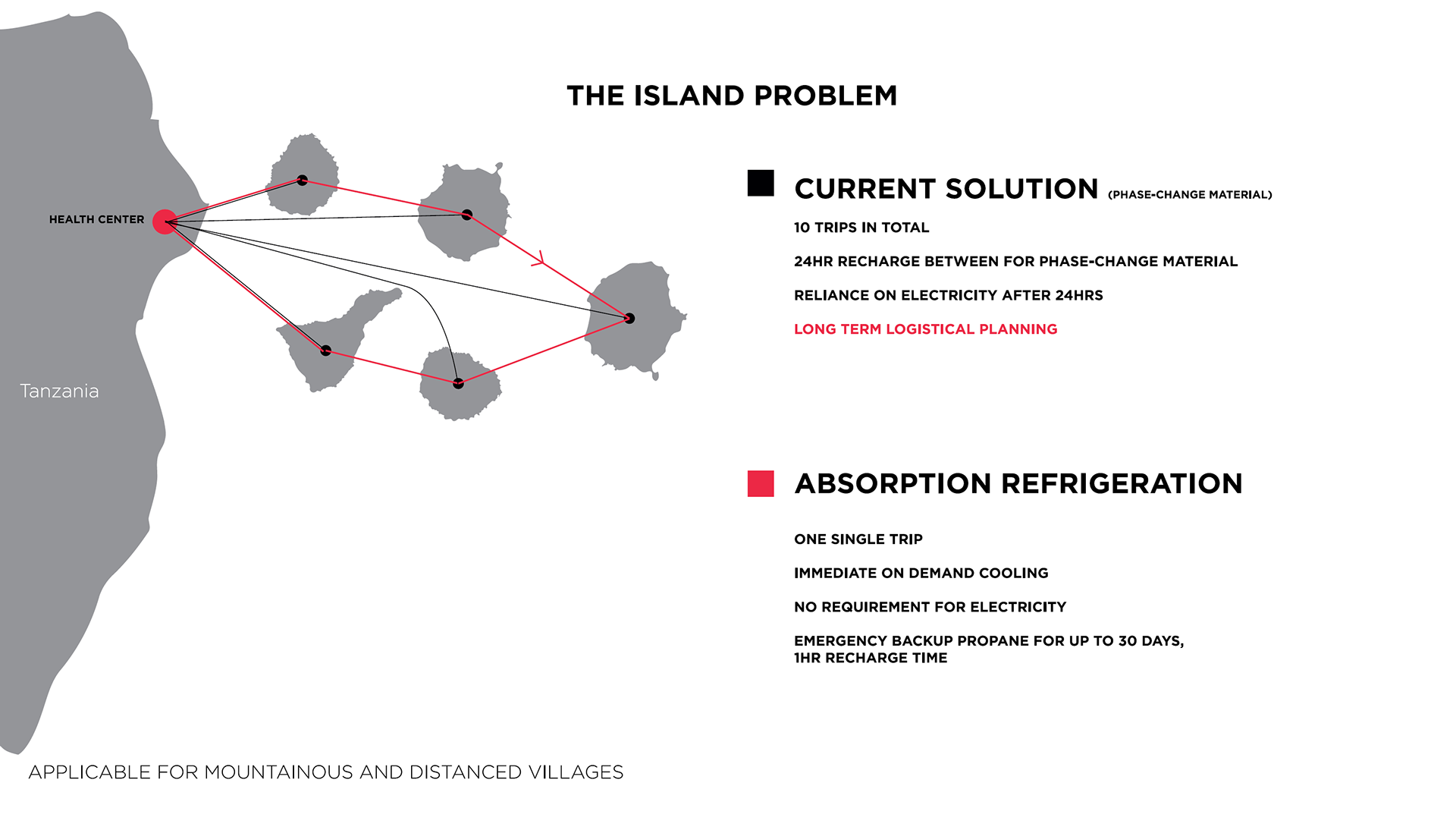
Issues in the last mile
Before starting my capstone project at Loughborough University, I travelled to Asia and read a book called 'From the killing fields to the healing fields' detailing Cambodia's struggle with last-mile delivery of vaccine. They had trouble simply keeping vaccine cool enough to administer which led to a huge number of lives lost.

Delivery by walkin
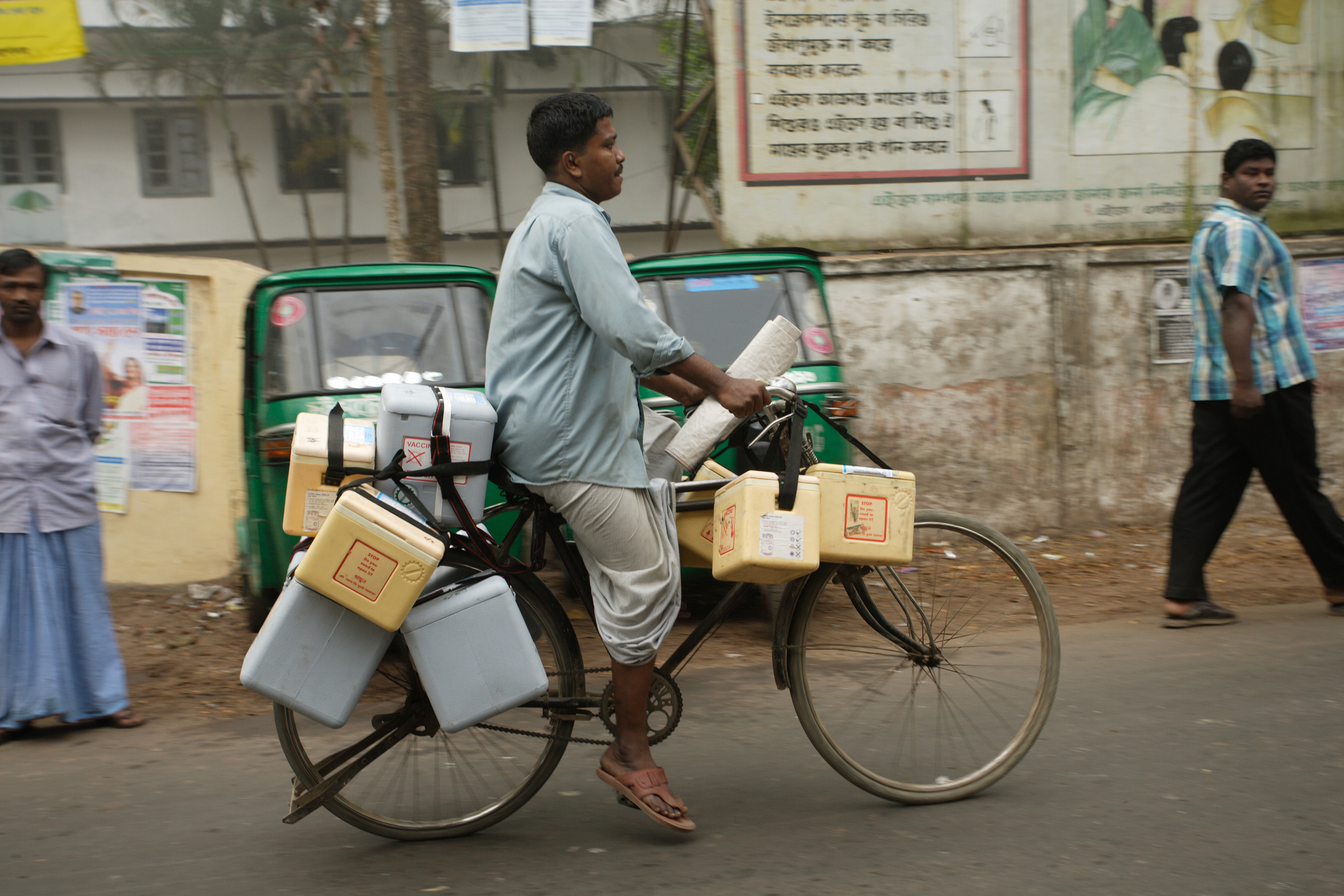

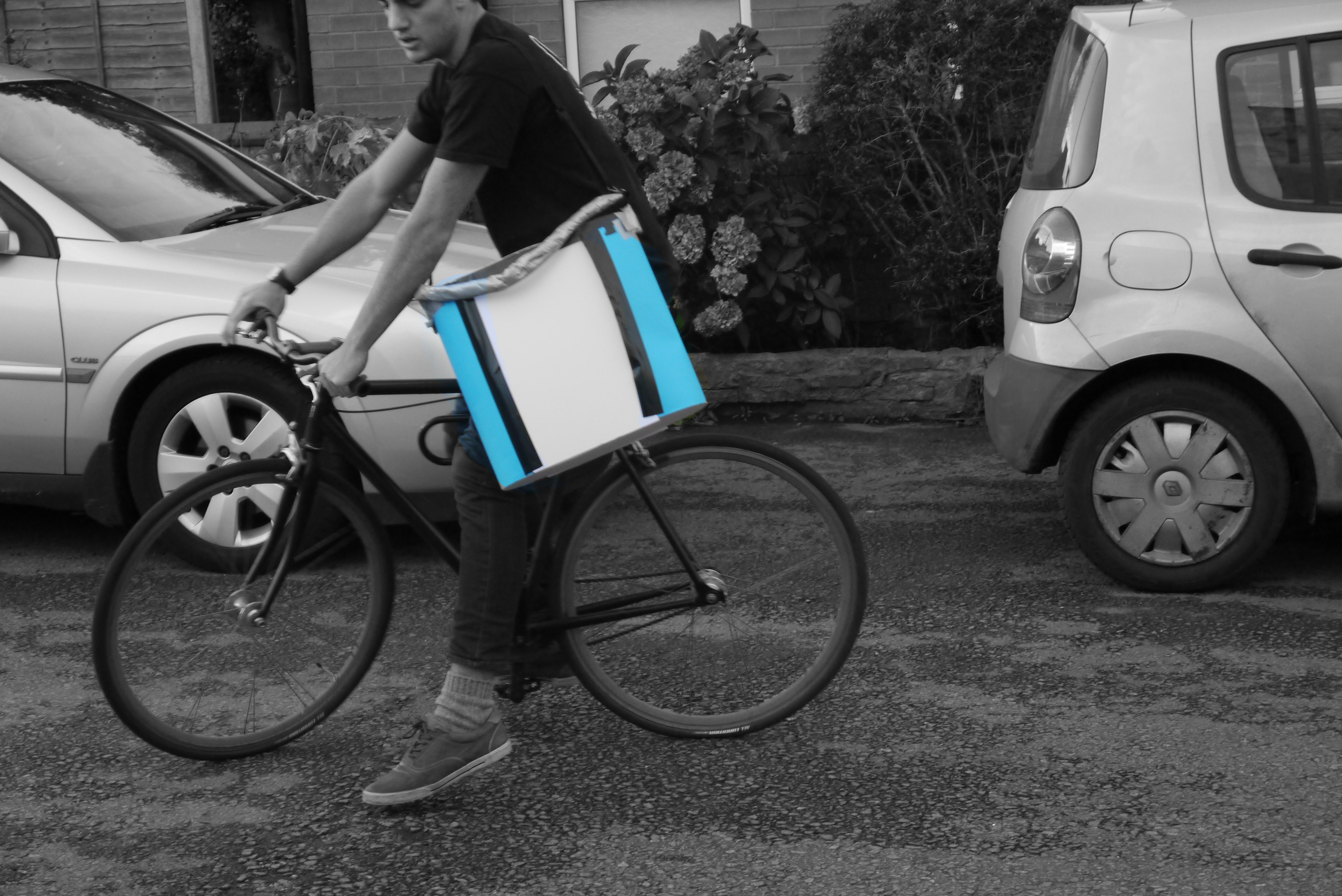
Delivery by bike
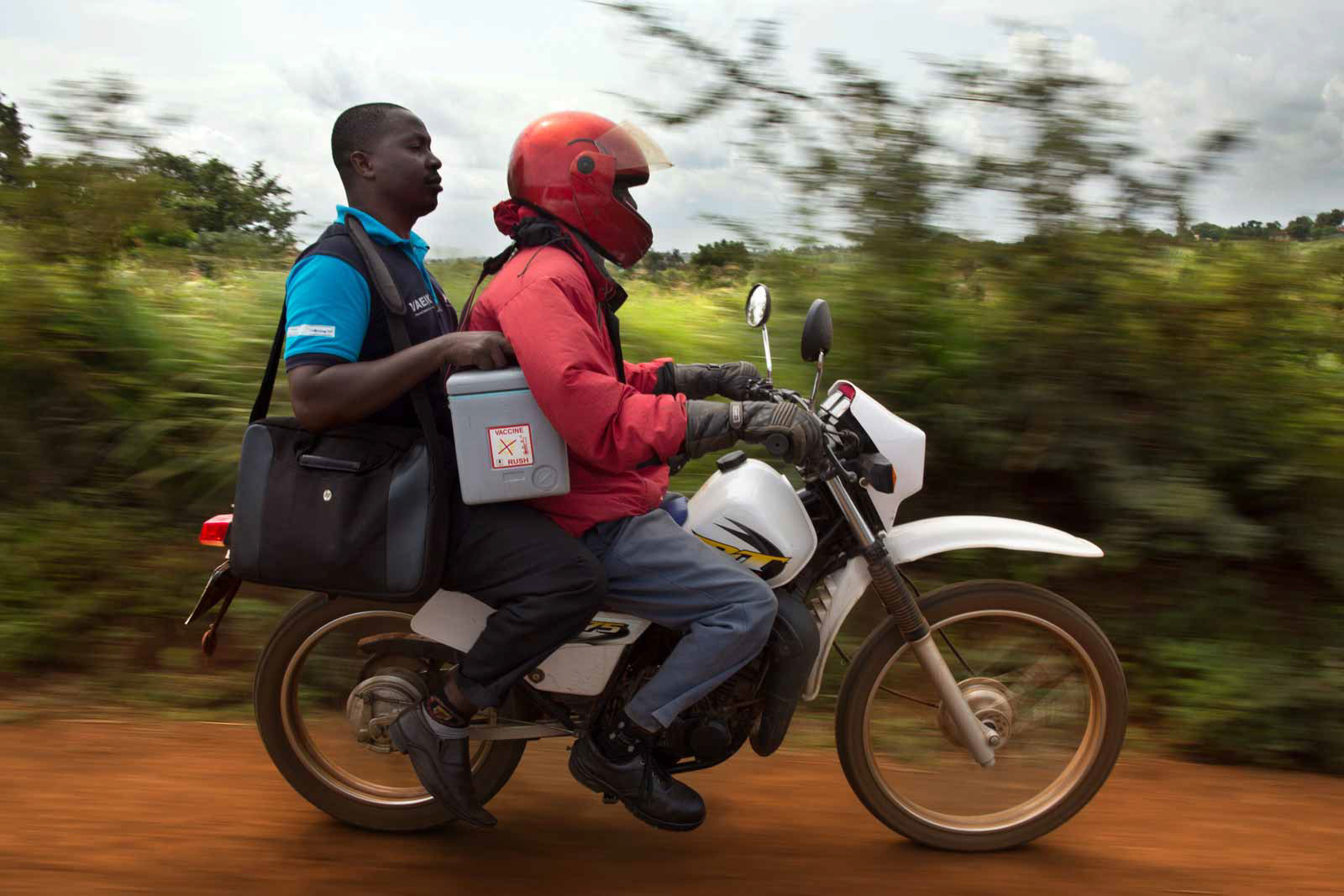

Delivery by vehicle
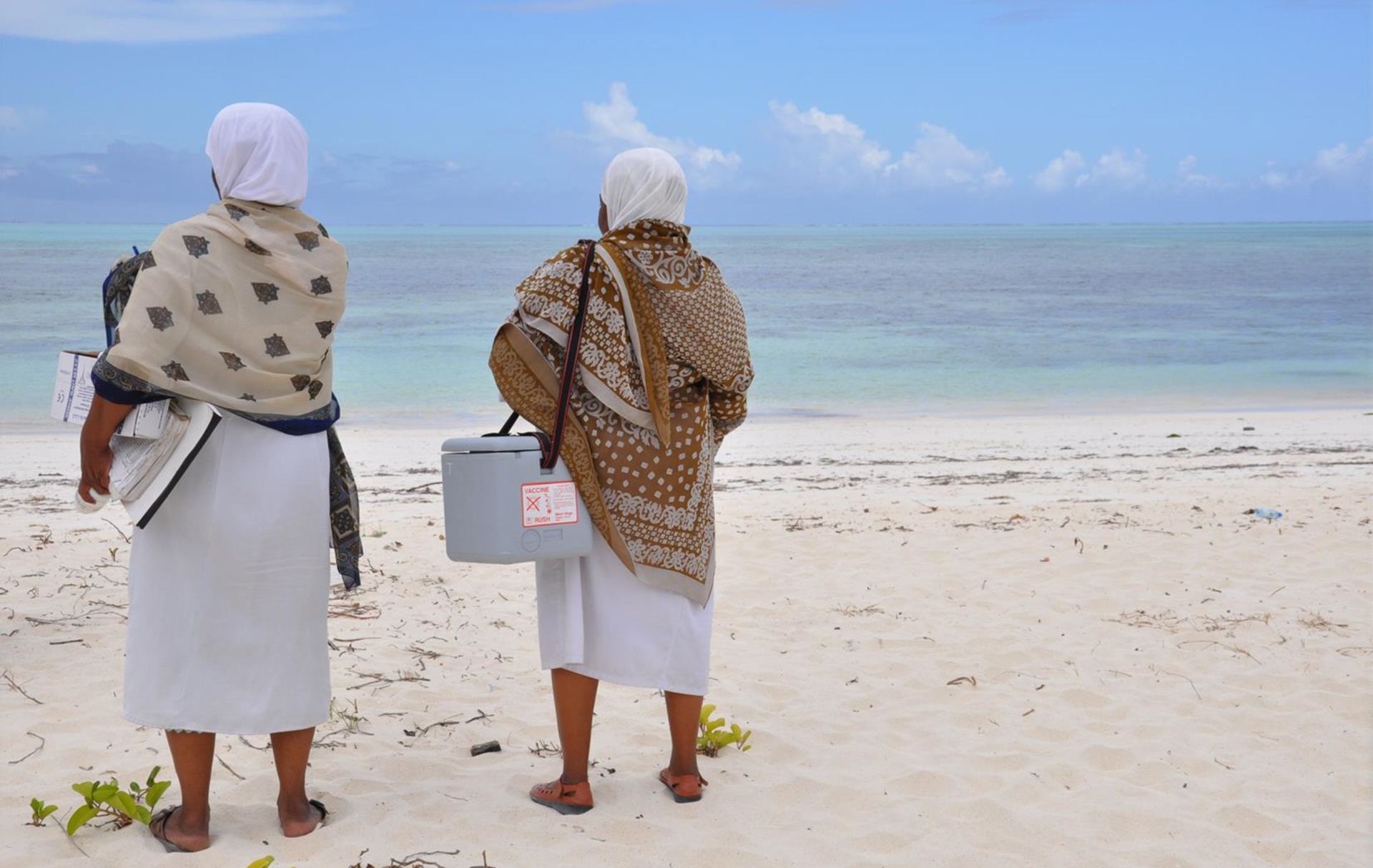

Remote delivery
Research
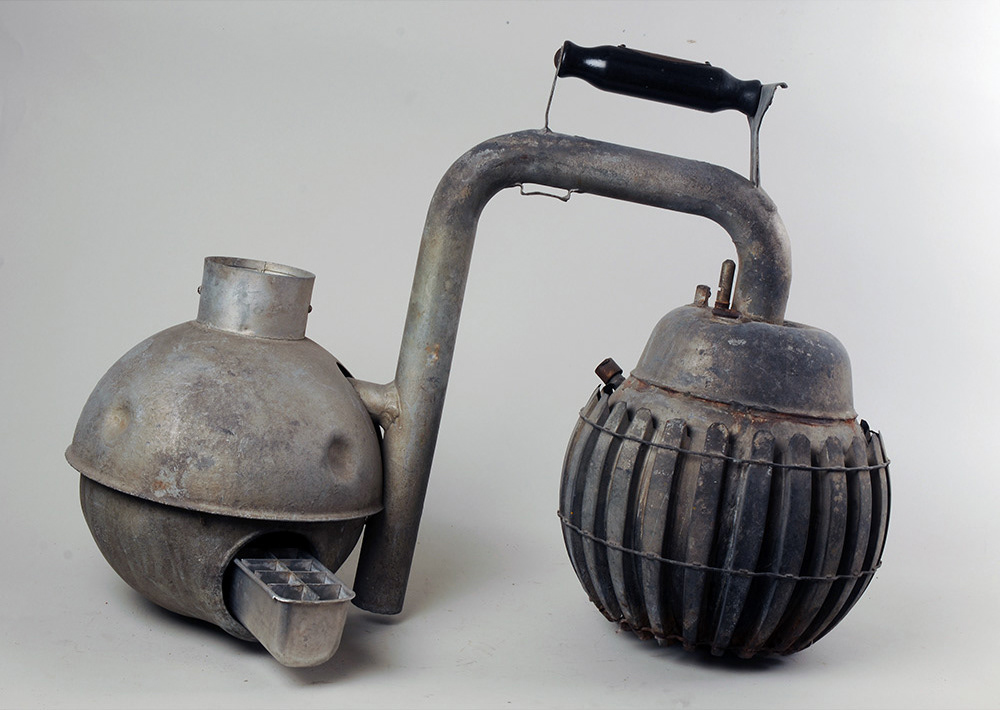
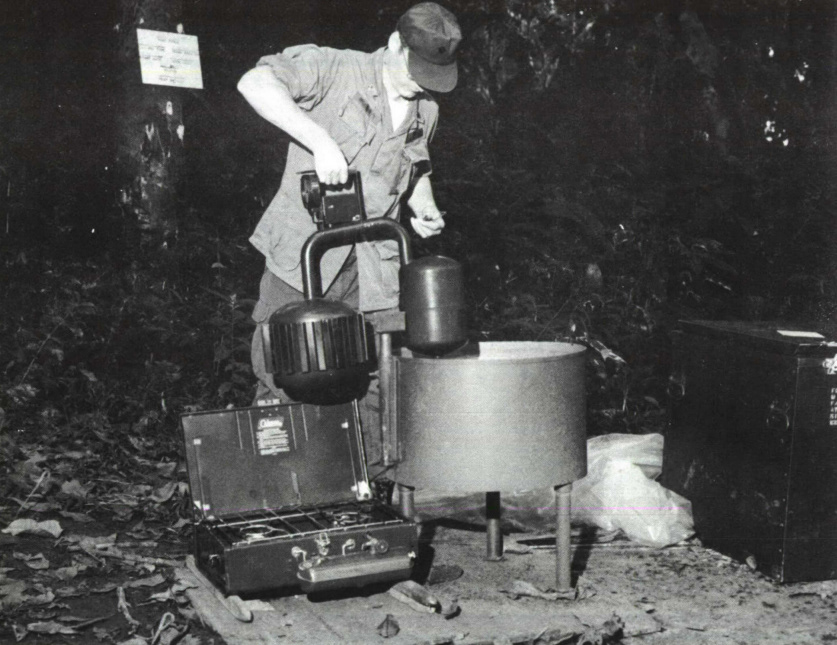
I looked into the scope of all available technologies for last mile delivery and stumbled upon the 1929 Crosley Icyball, used for rural farming refrigeration before widespread adoption of electric fridges, it was cast iron and weighed 50Kg.
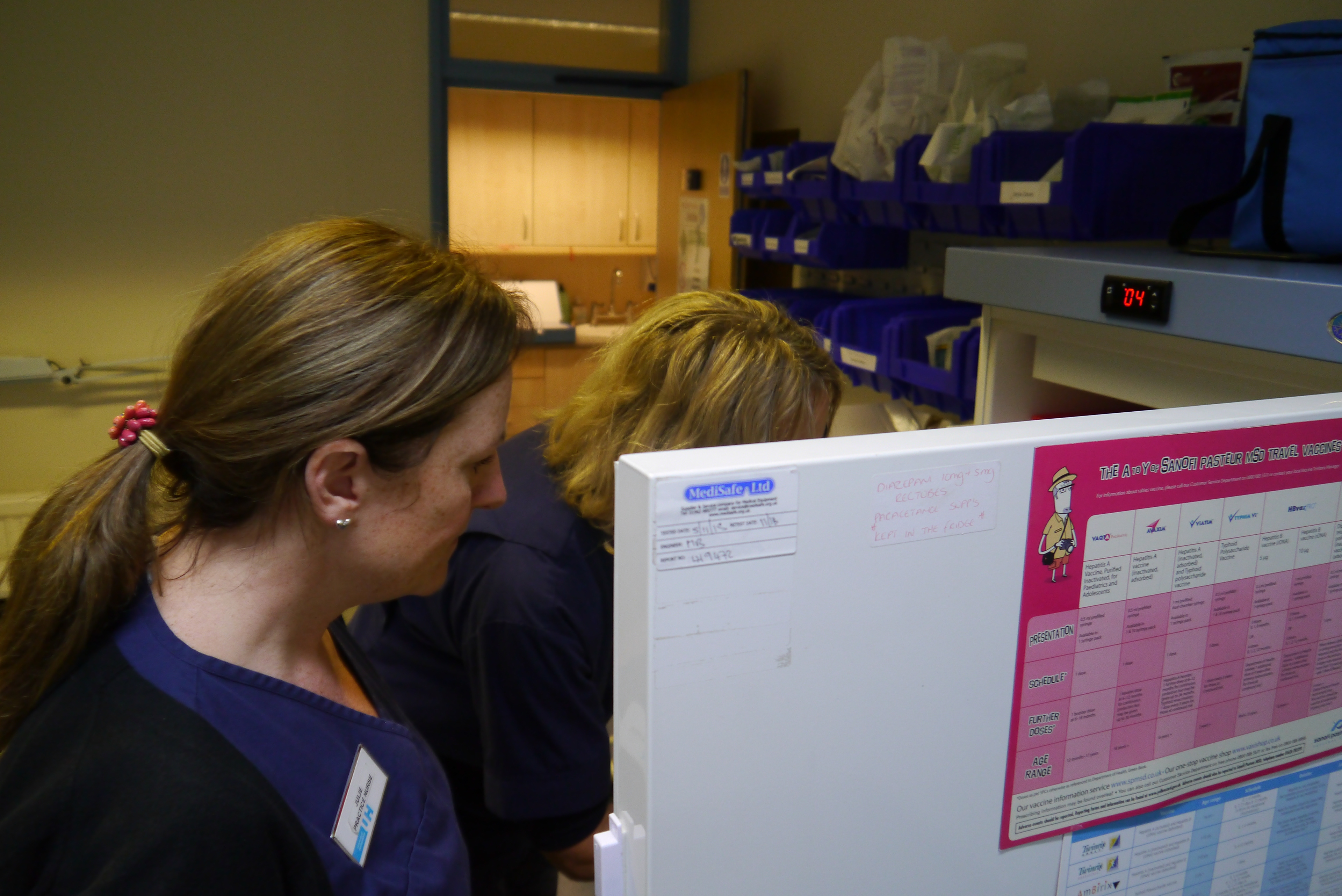
I contacted a group of nurse practitioners specifically working on vaccine delivery in the UK. With their insights, I identified critical issues in vaccine infrastructure that pinpointed last-mile delivery as a core problem even in developed nations.
Through these insights I mapped all of the key issues and started developing an ergonomic understanding of the type of device and payload required to do the job.



Recording user journey

Learning about full vaccine process

Mapping the user journey
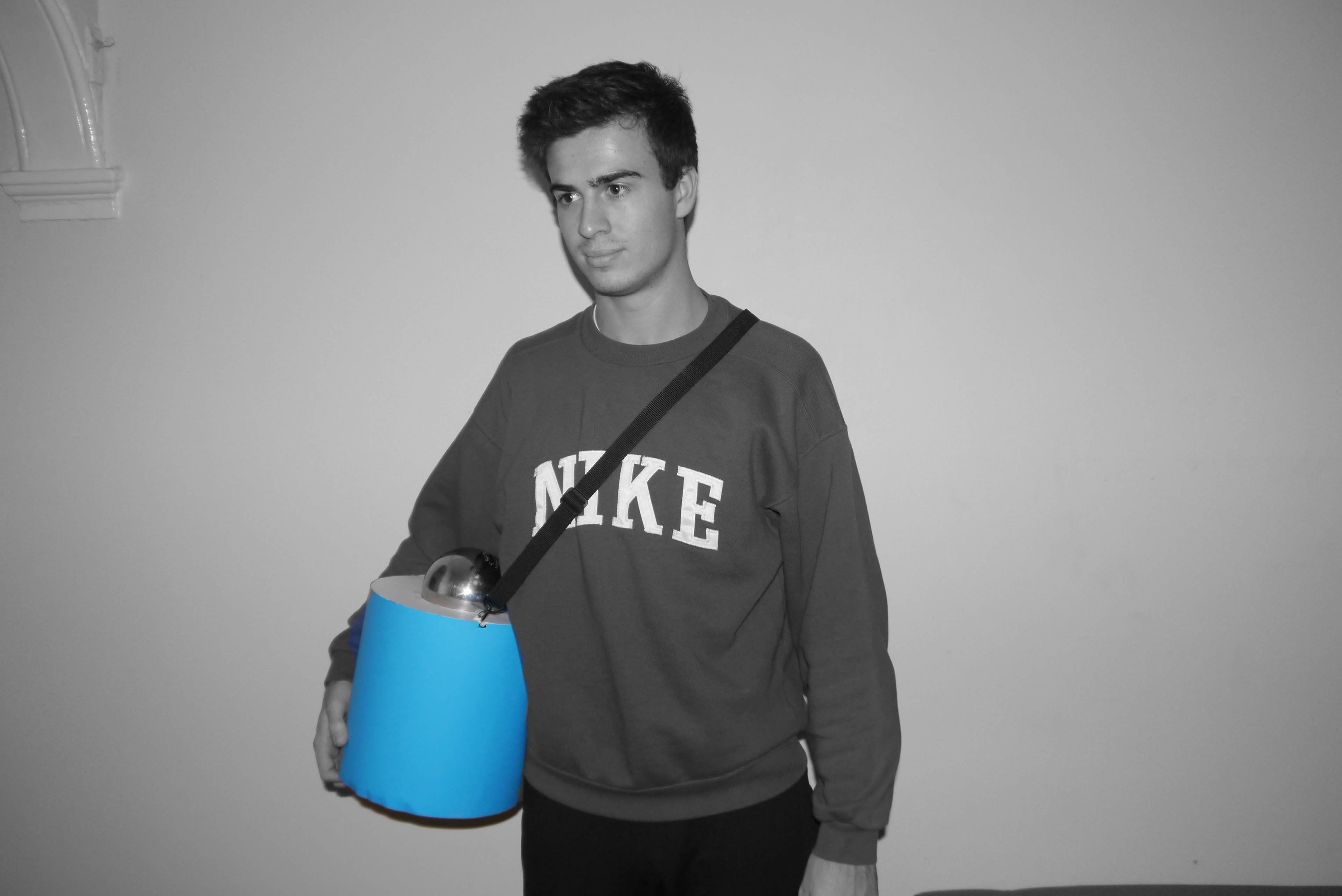

Paper prototype carrier

Paper prototype 2
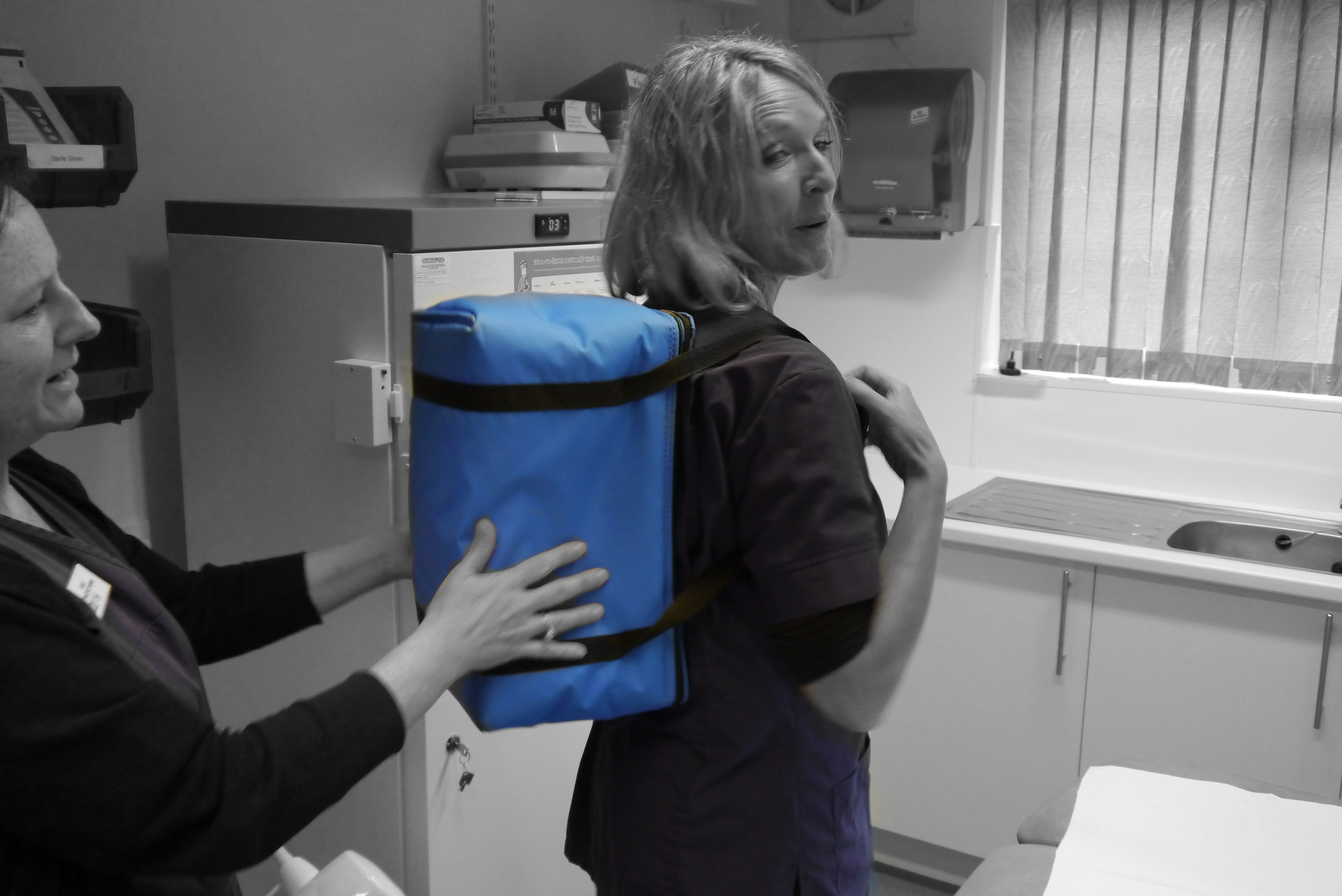
Testing base ergonomics
Identifying the opportunity
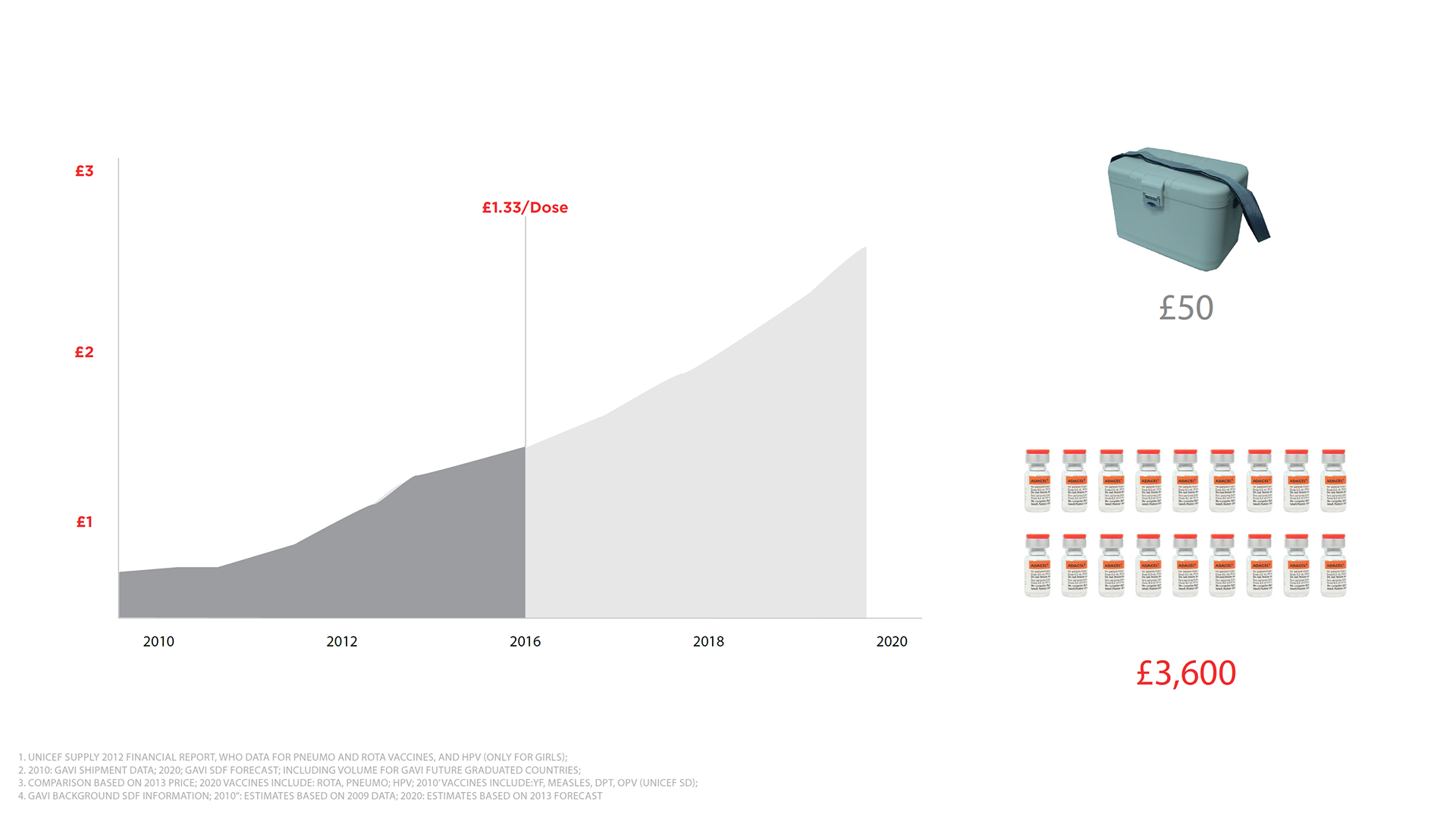
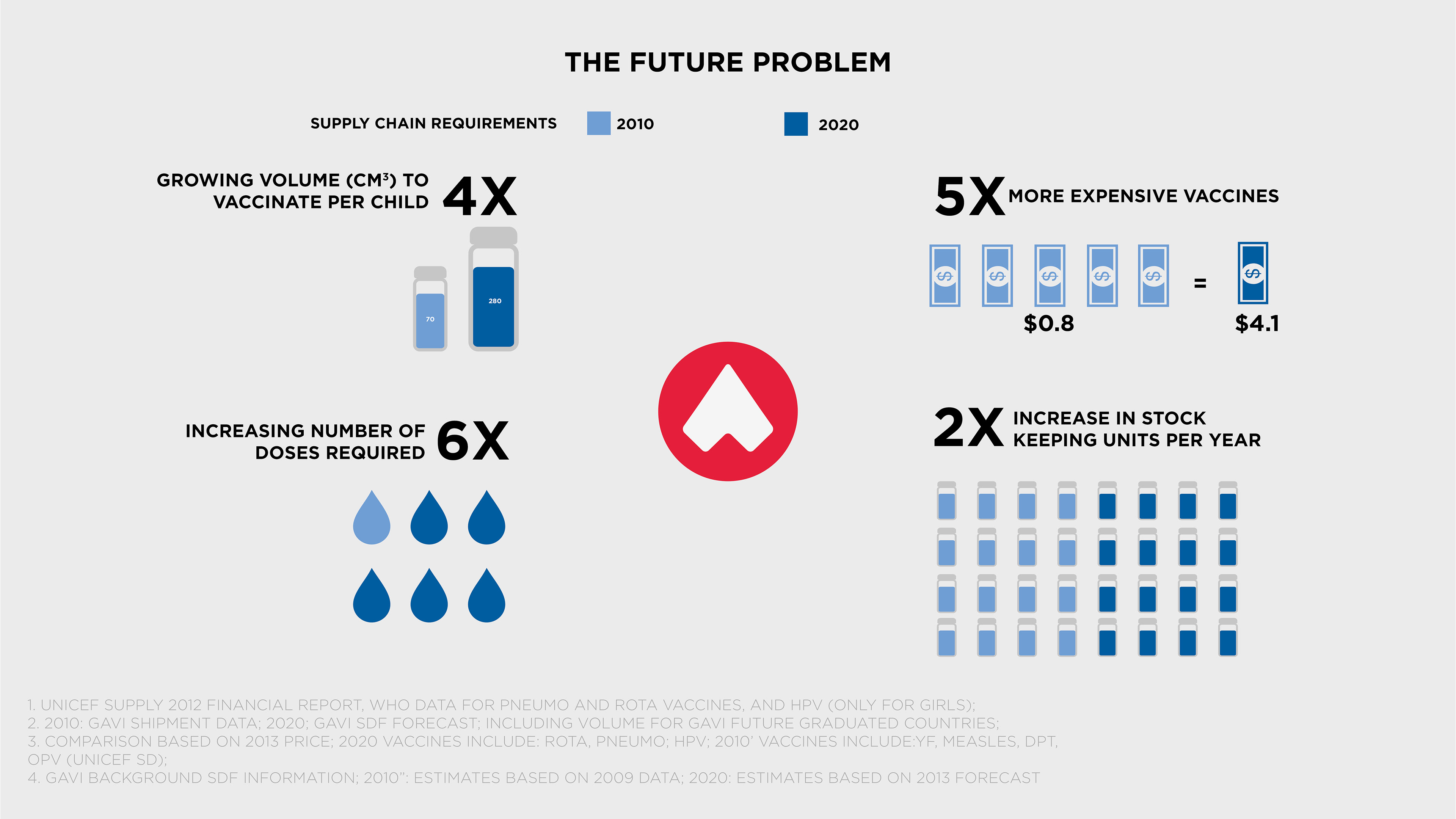
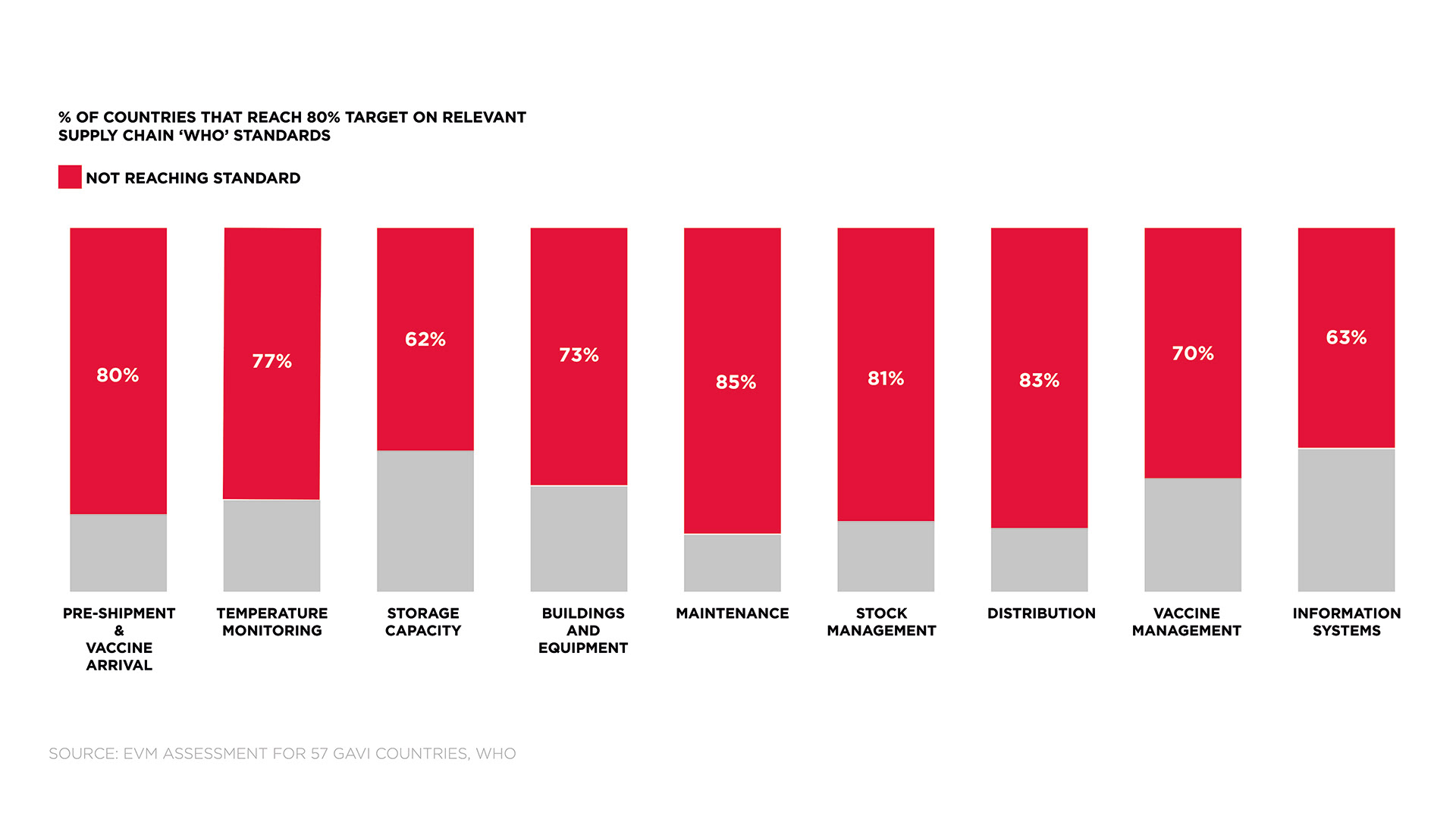
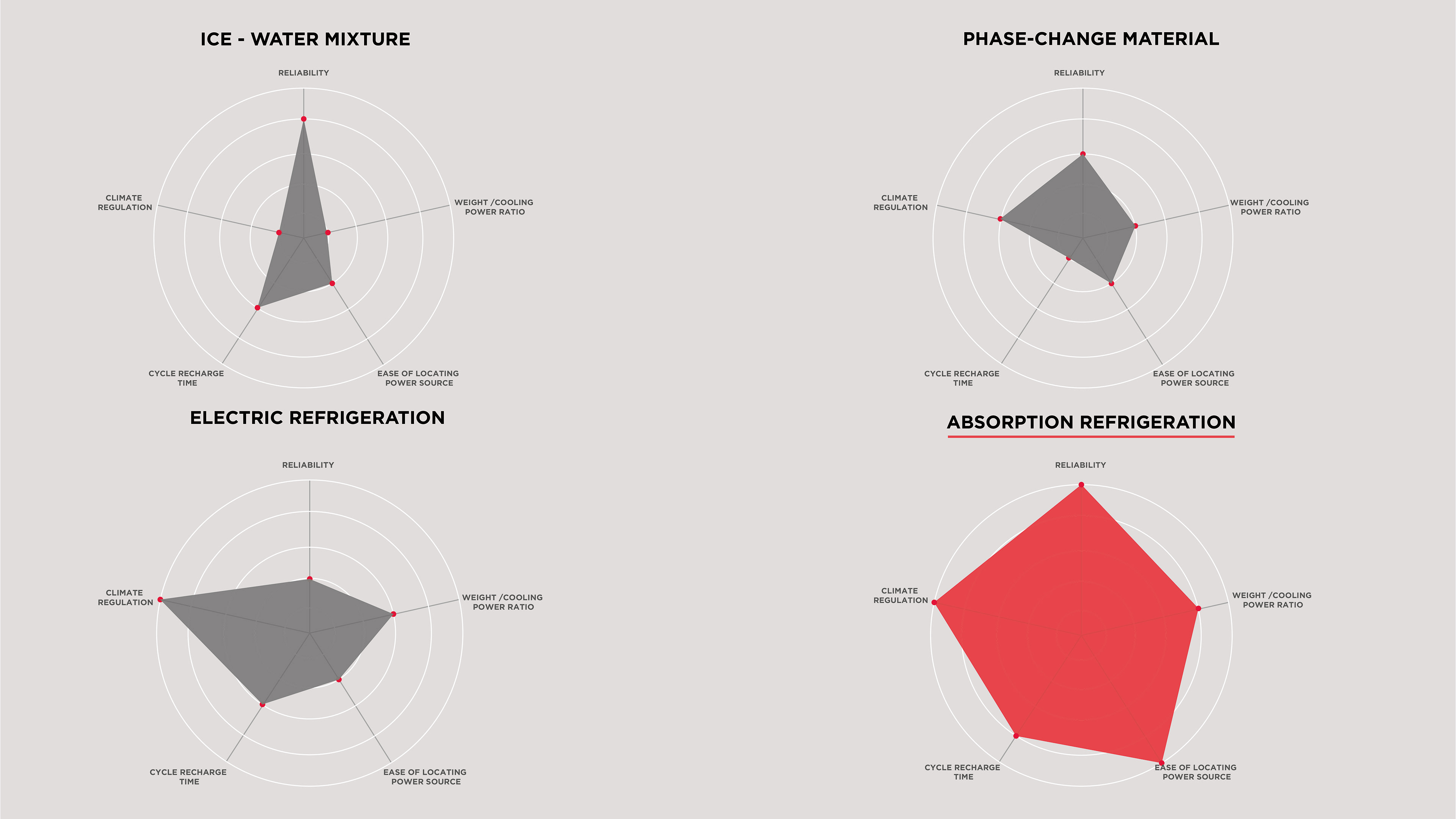
I read studies conducted by leading global vaccine governing bodies such as PATH, GAVI, Gates Foundation and WHO. Insights taught me that the best carrier in the world would only provide 2-8C cooling for 7.5hrs. This issue alone was a major contributor to distributors losing millions of dollars in expensive vaccine with each payload that spoiled a loss of $3600.

Usability models
I designed many different kinds of models to assess how the device will be used by nurses in the field.
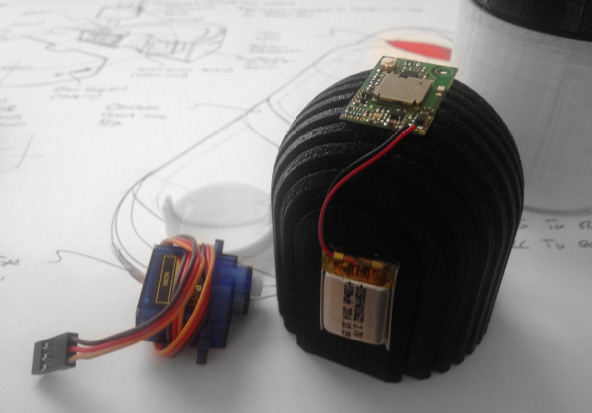
Scale model electronic mockup
Assembly scale model
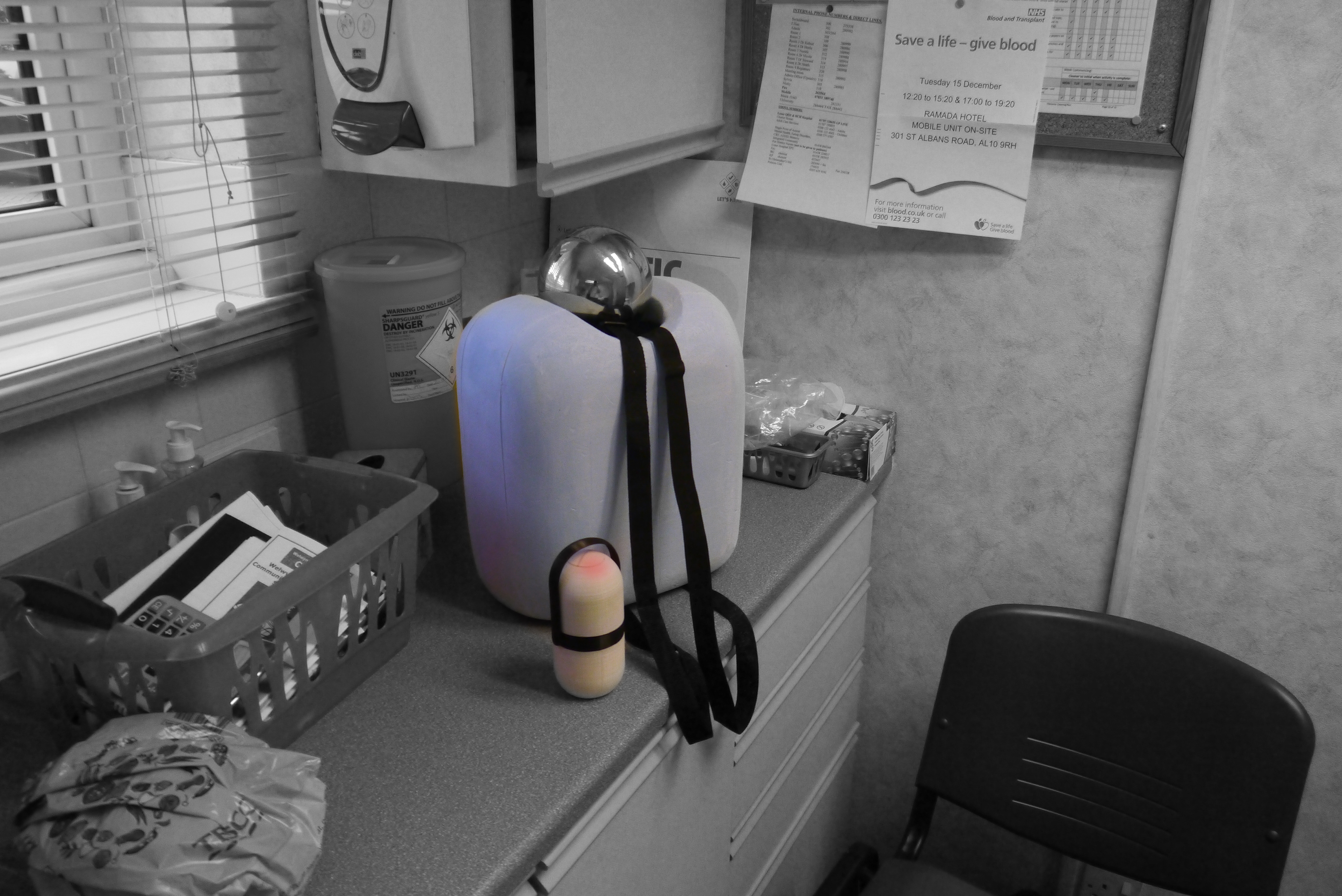
Scale model+ backpack in user testing
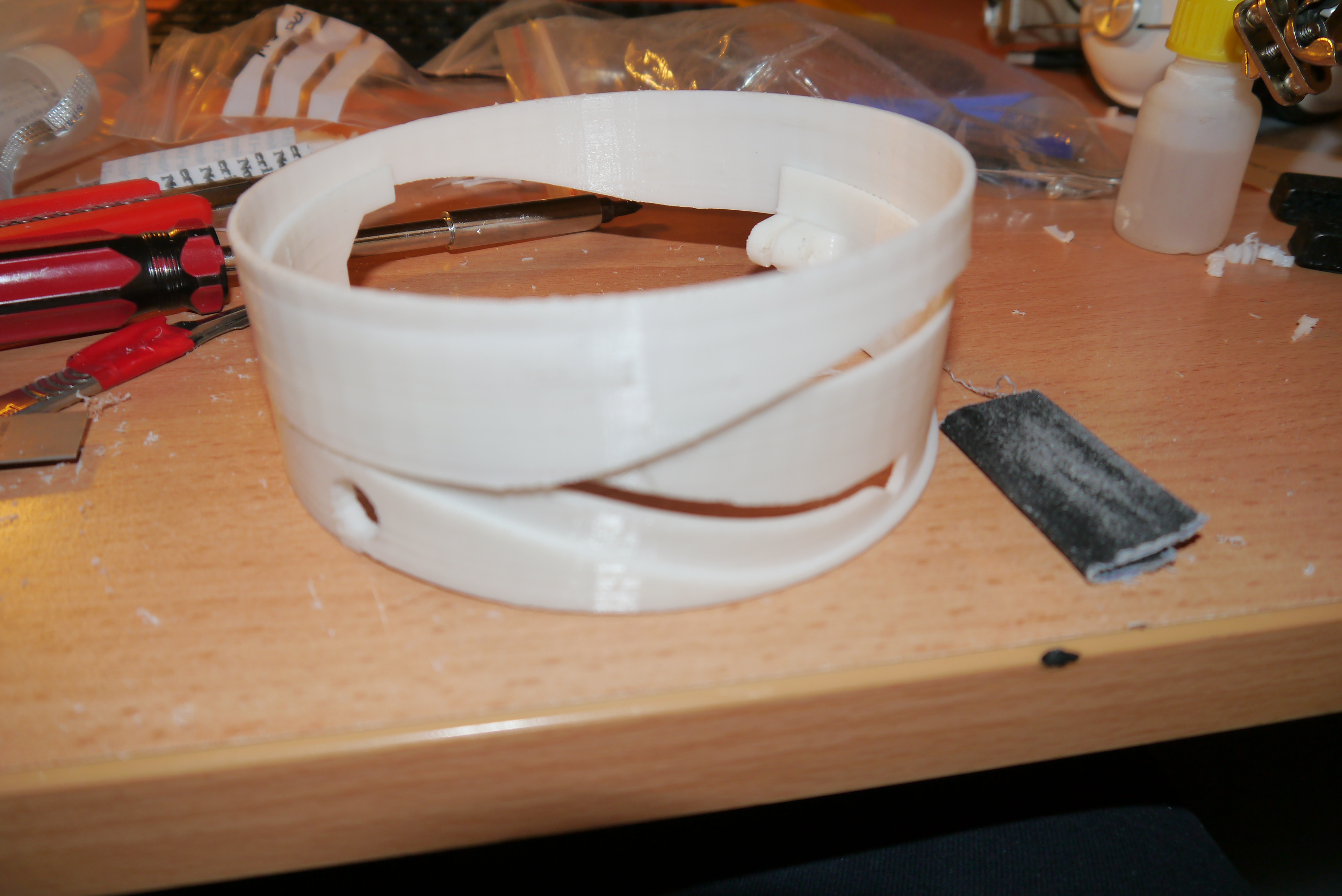

Mechanism prototype
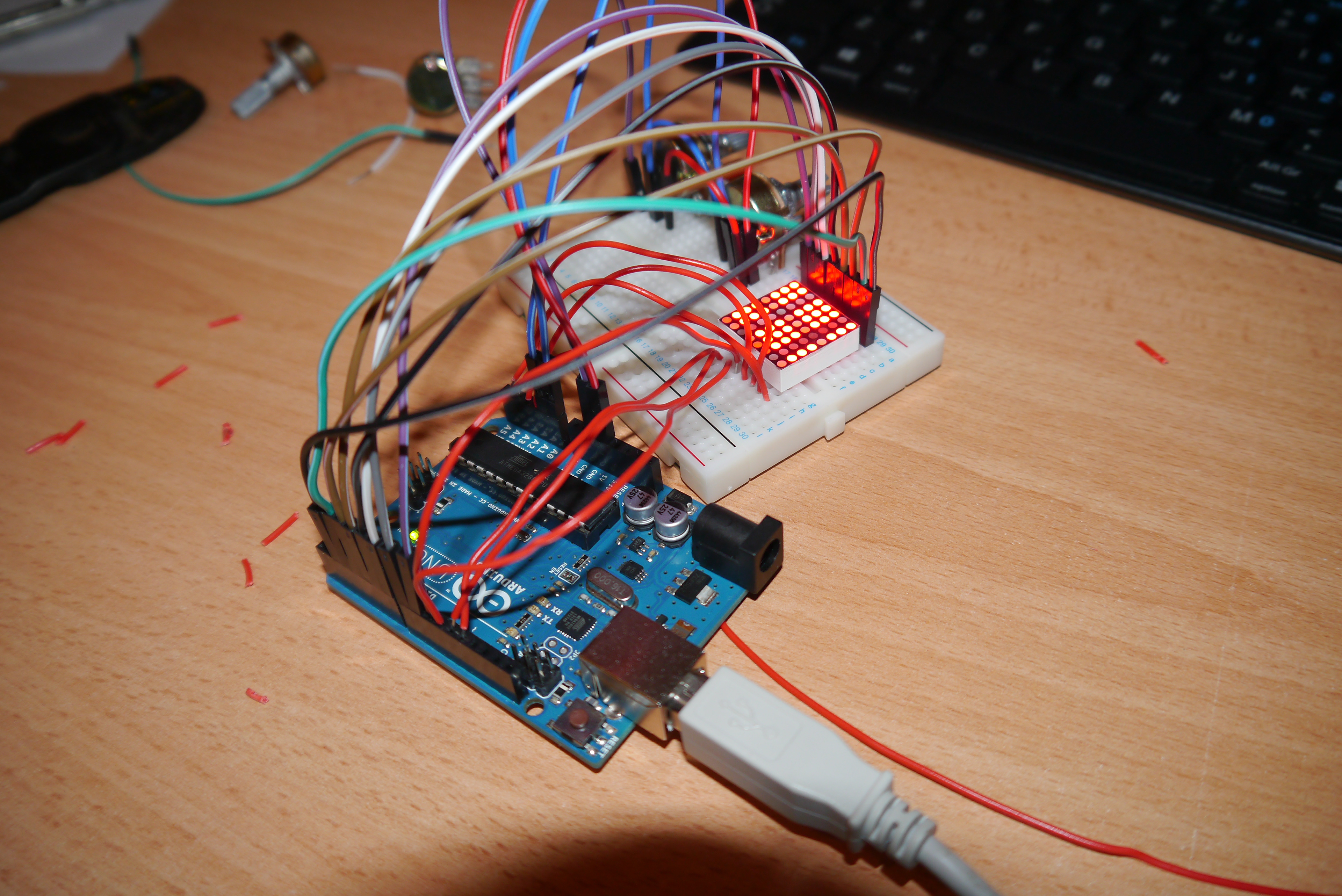
Electronic development
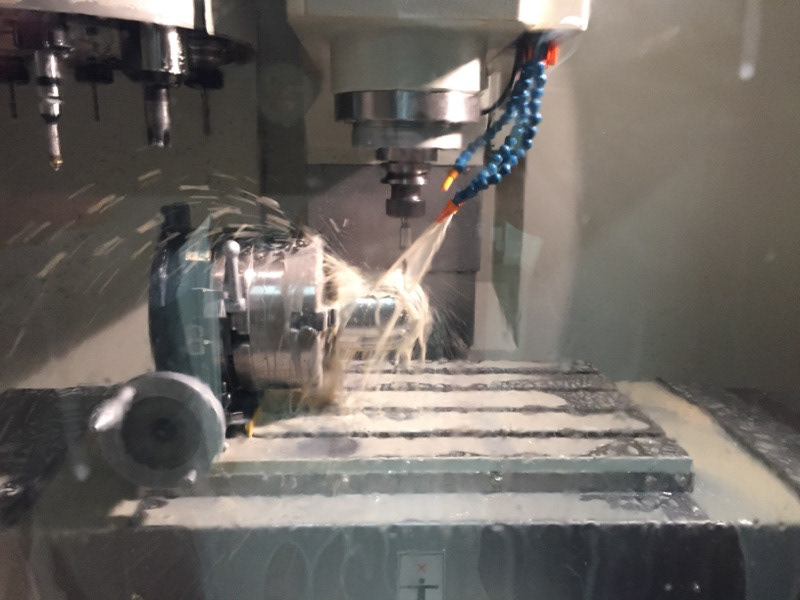

Coding my own mill operations
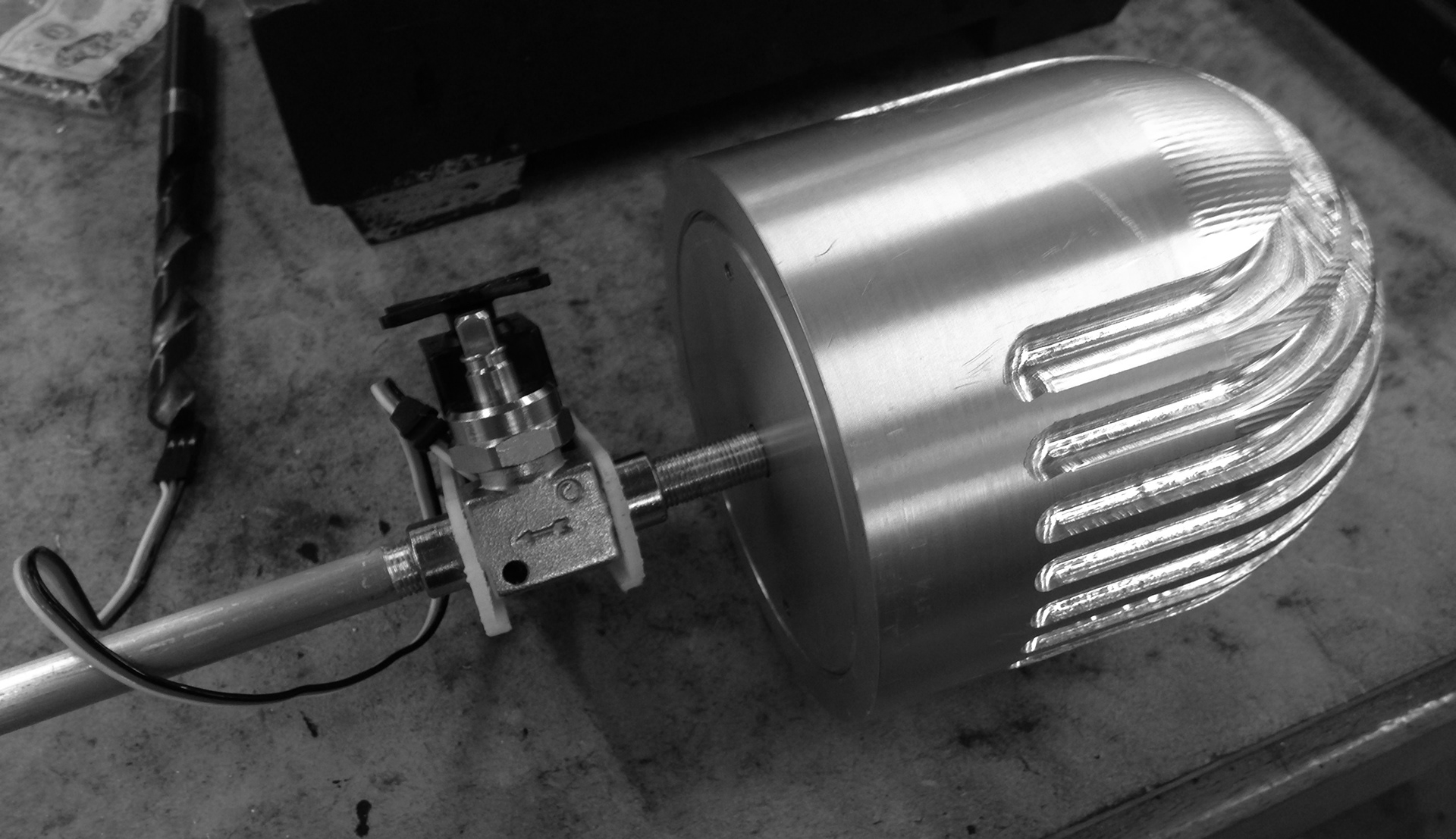

Partial assembly after milling
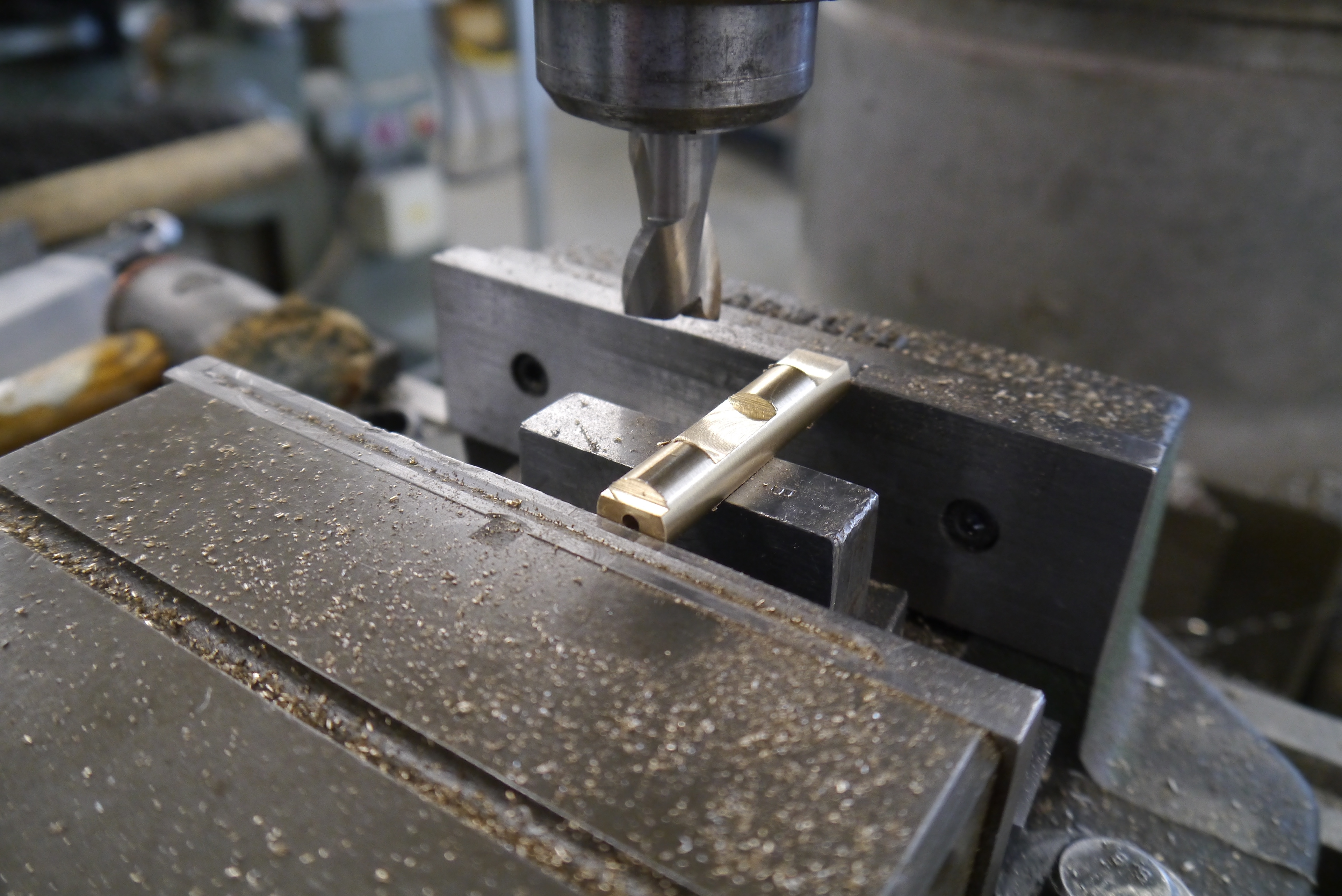

Hand fabrication of brass pivots
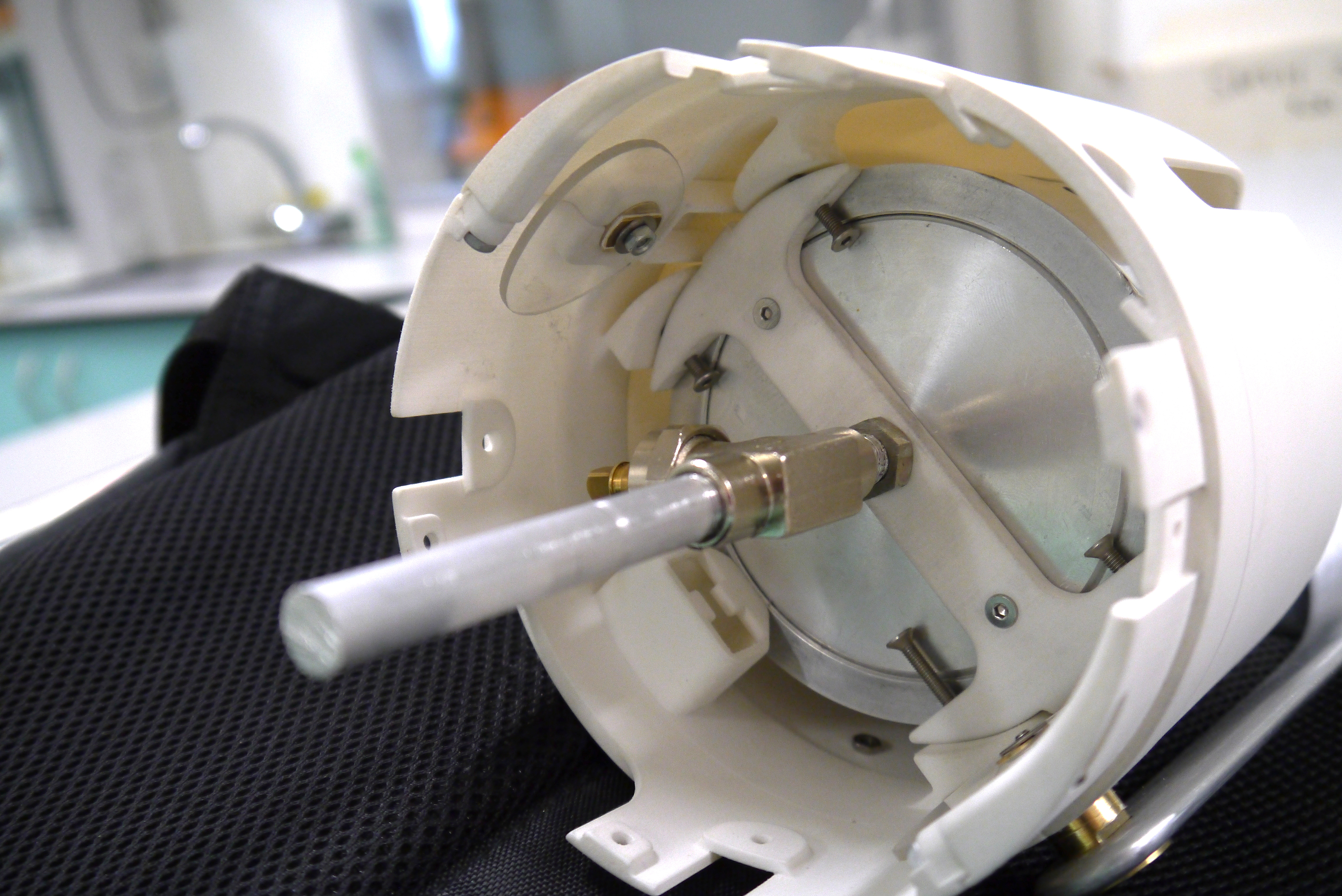
3D print assembly
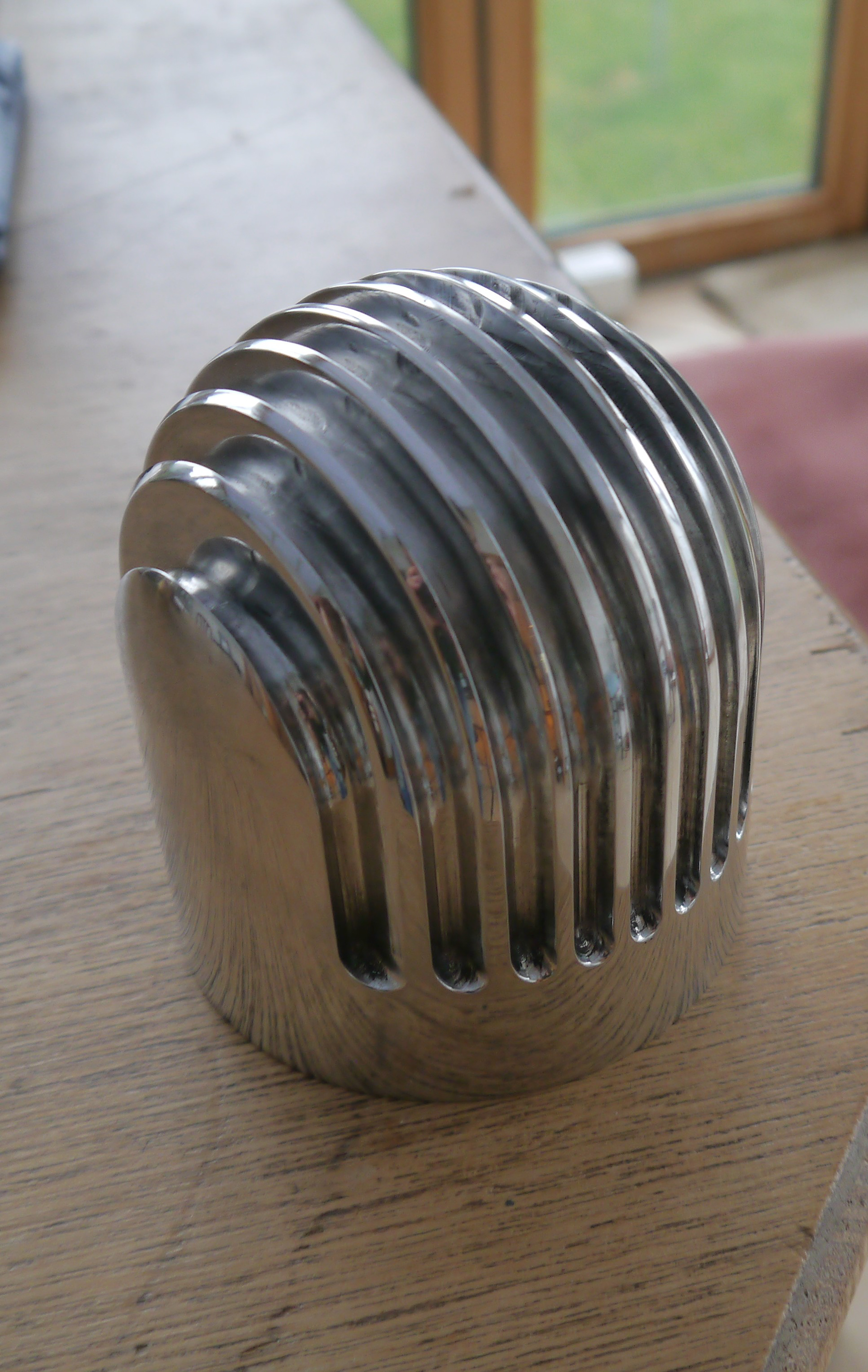

Polished heatsink
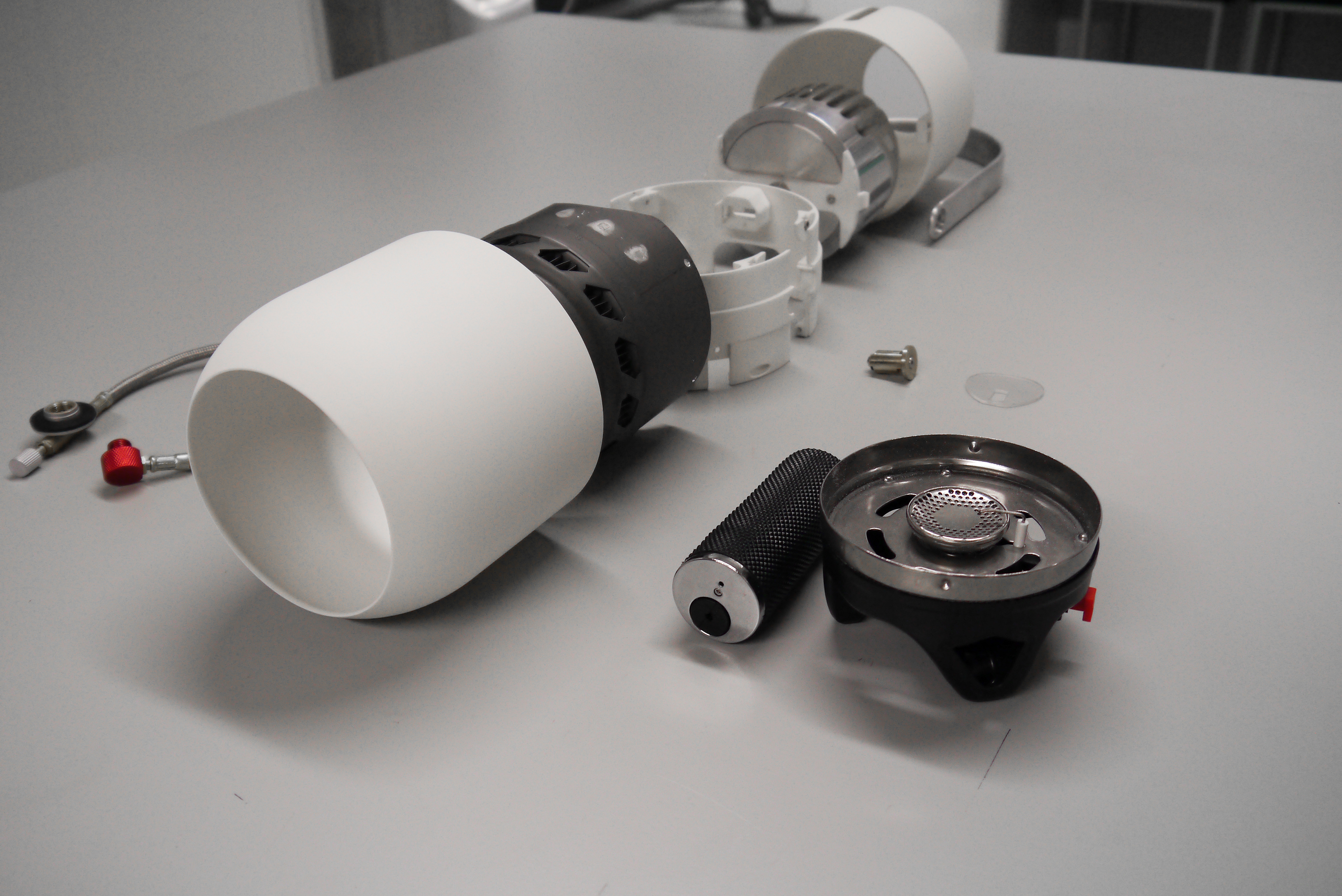

Prototype parts for assembly
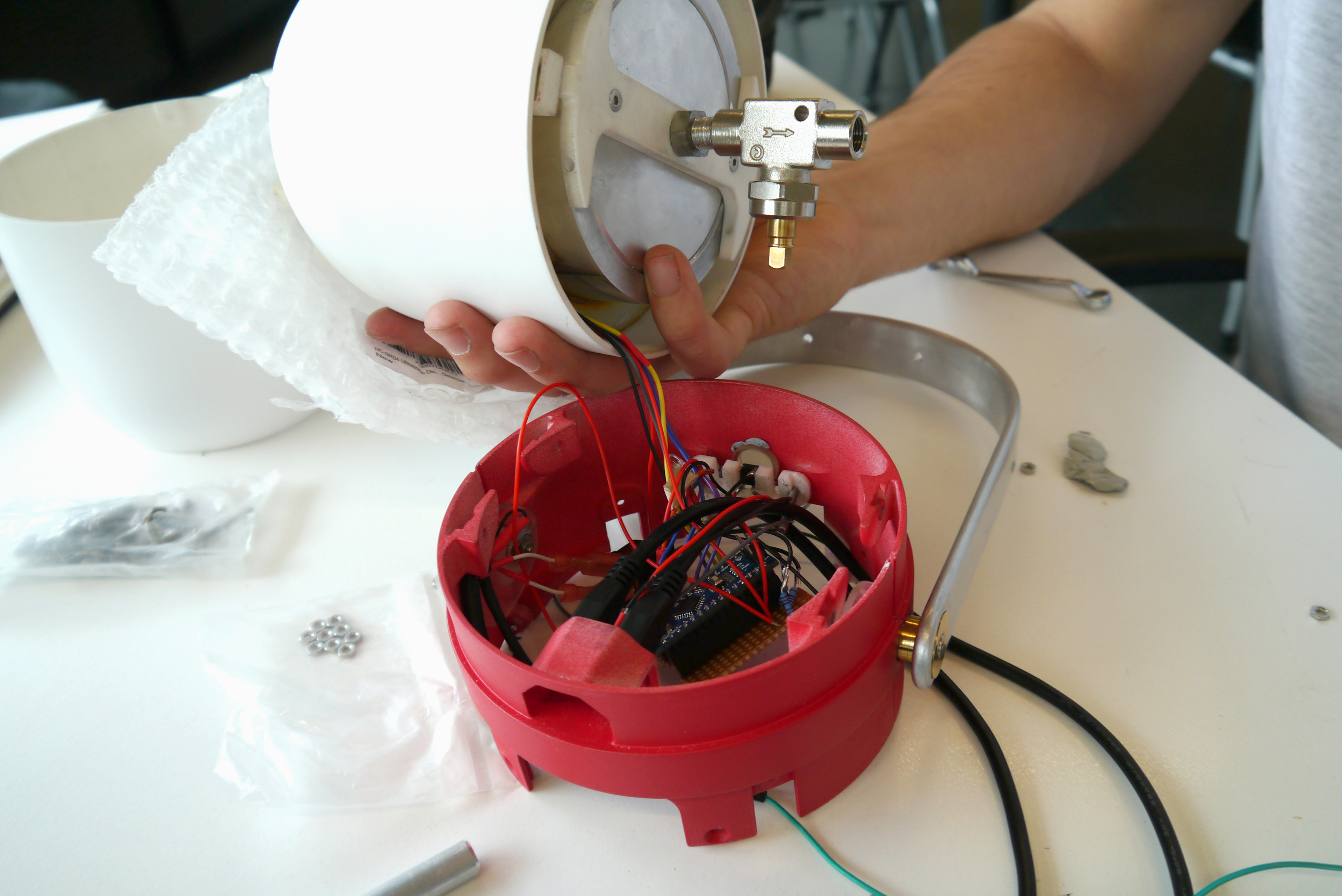
Prototype electronics
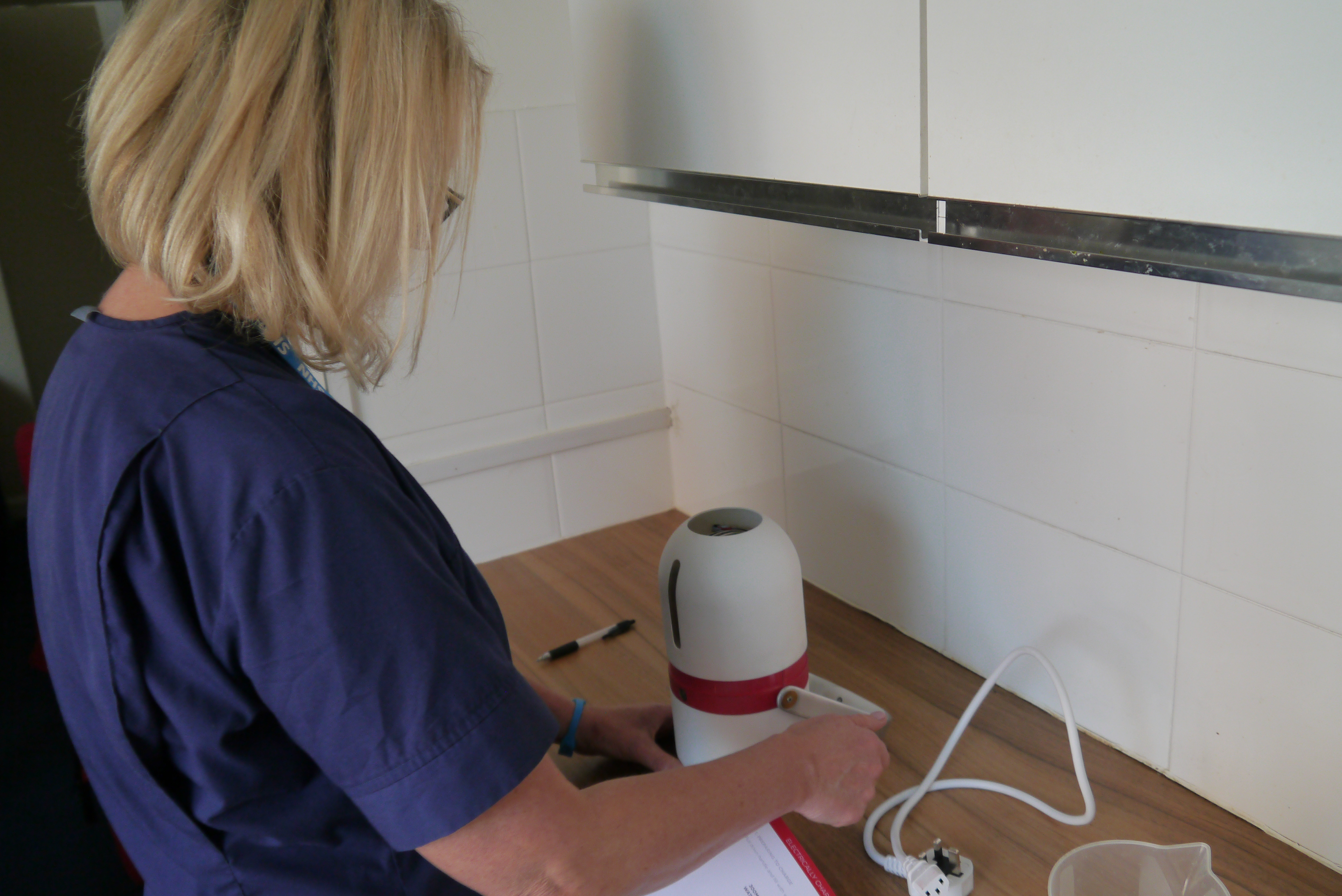
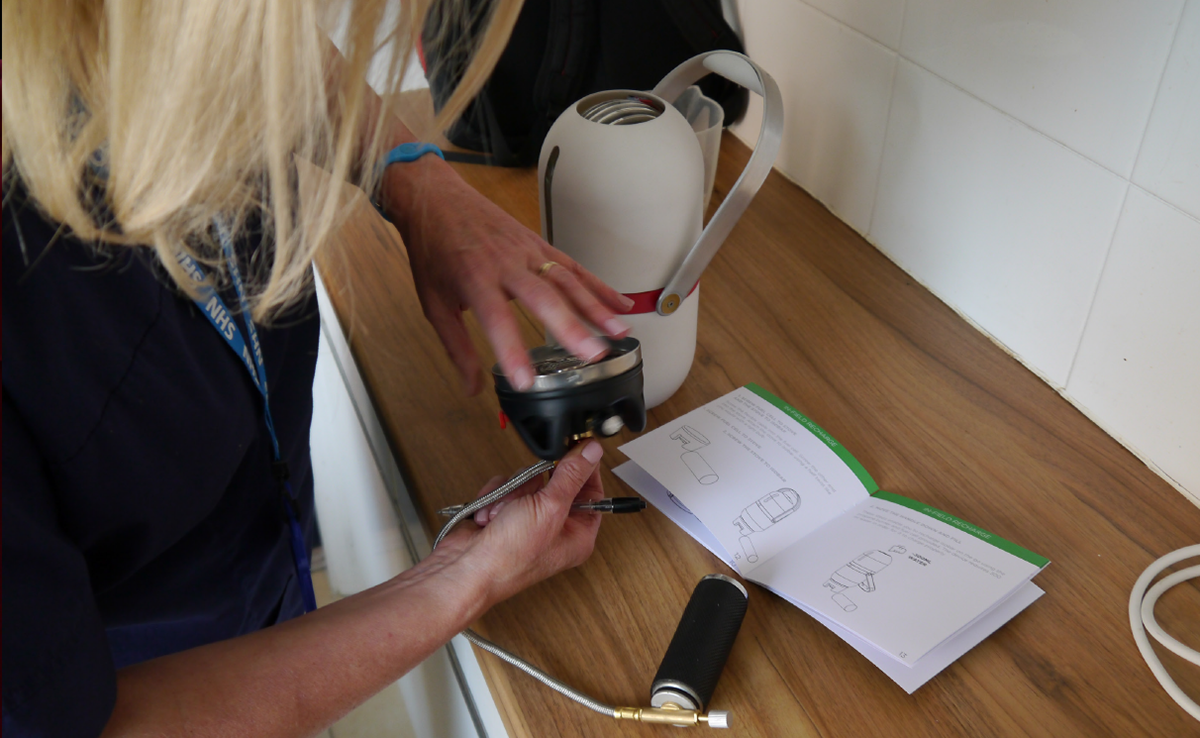
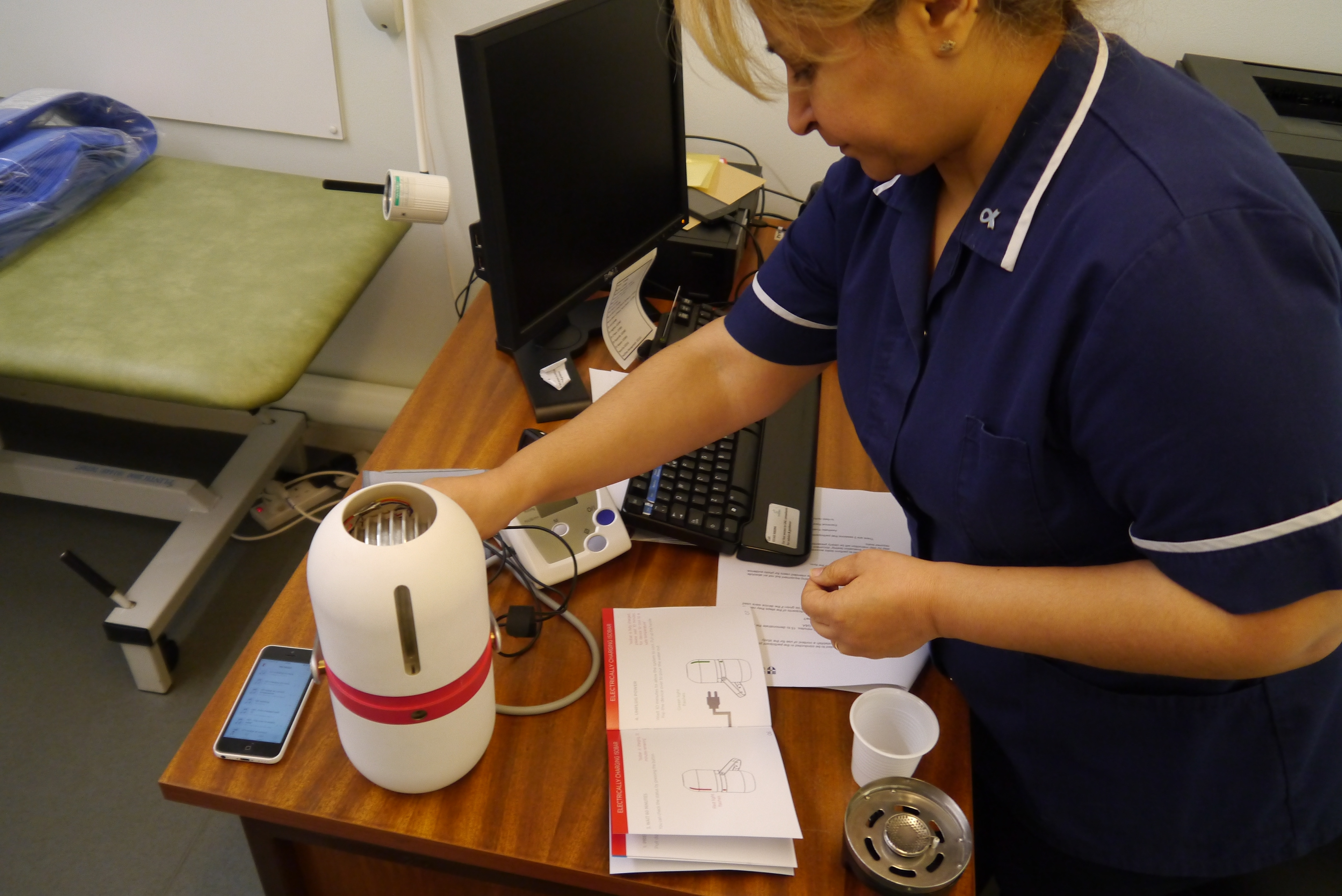
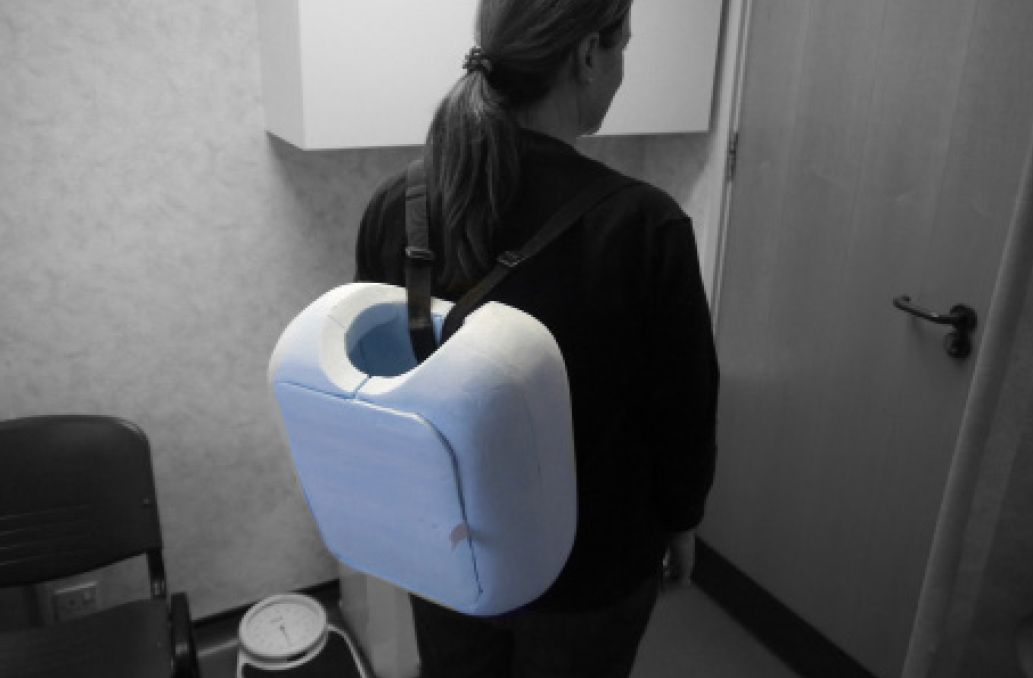
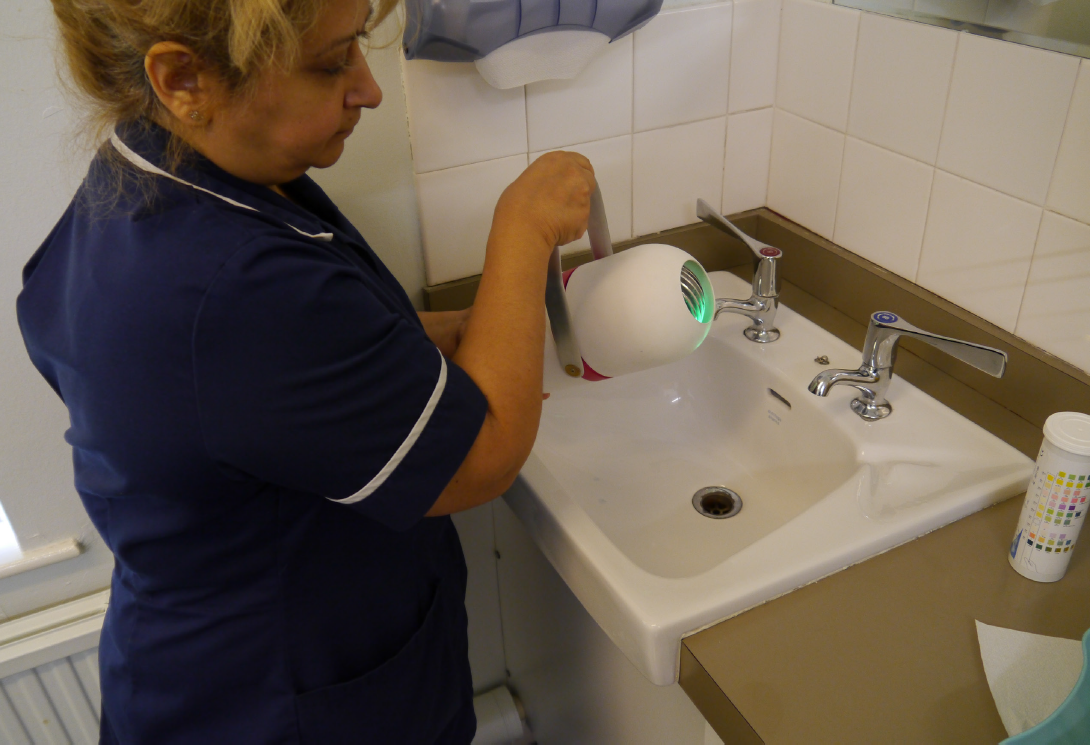
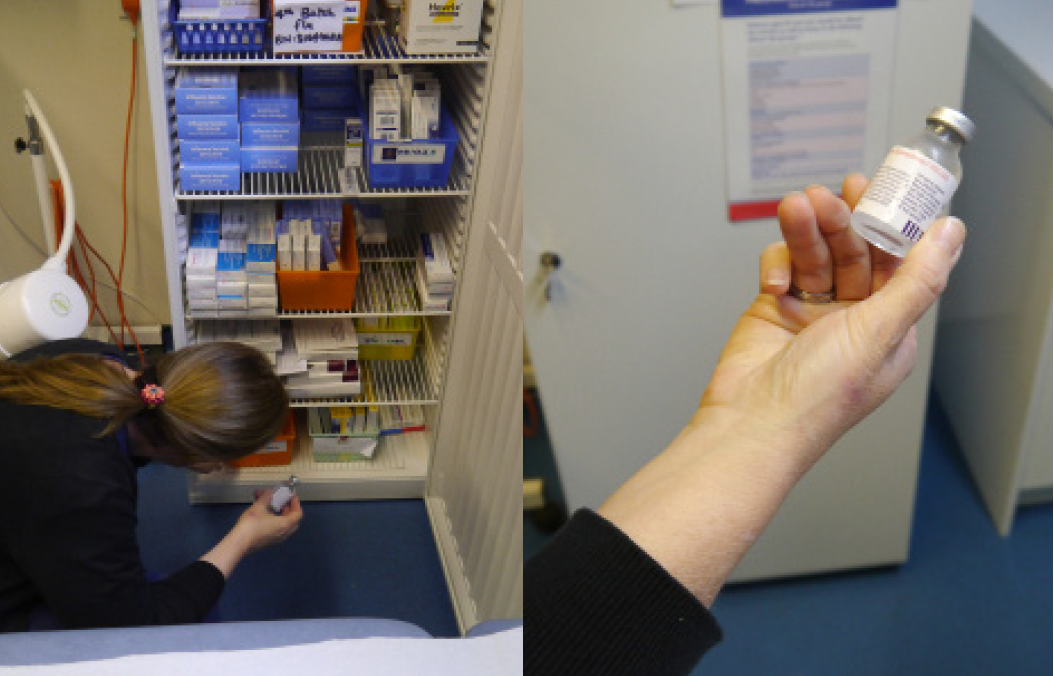
Design validation with nurses
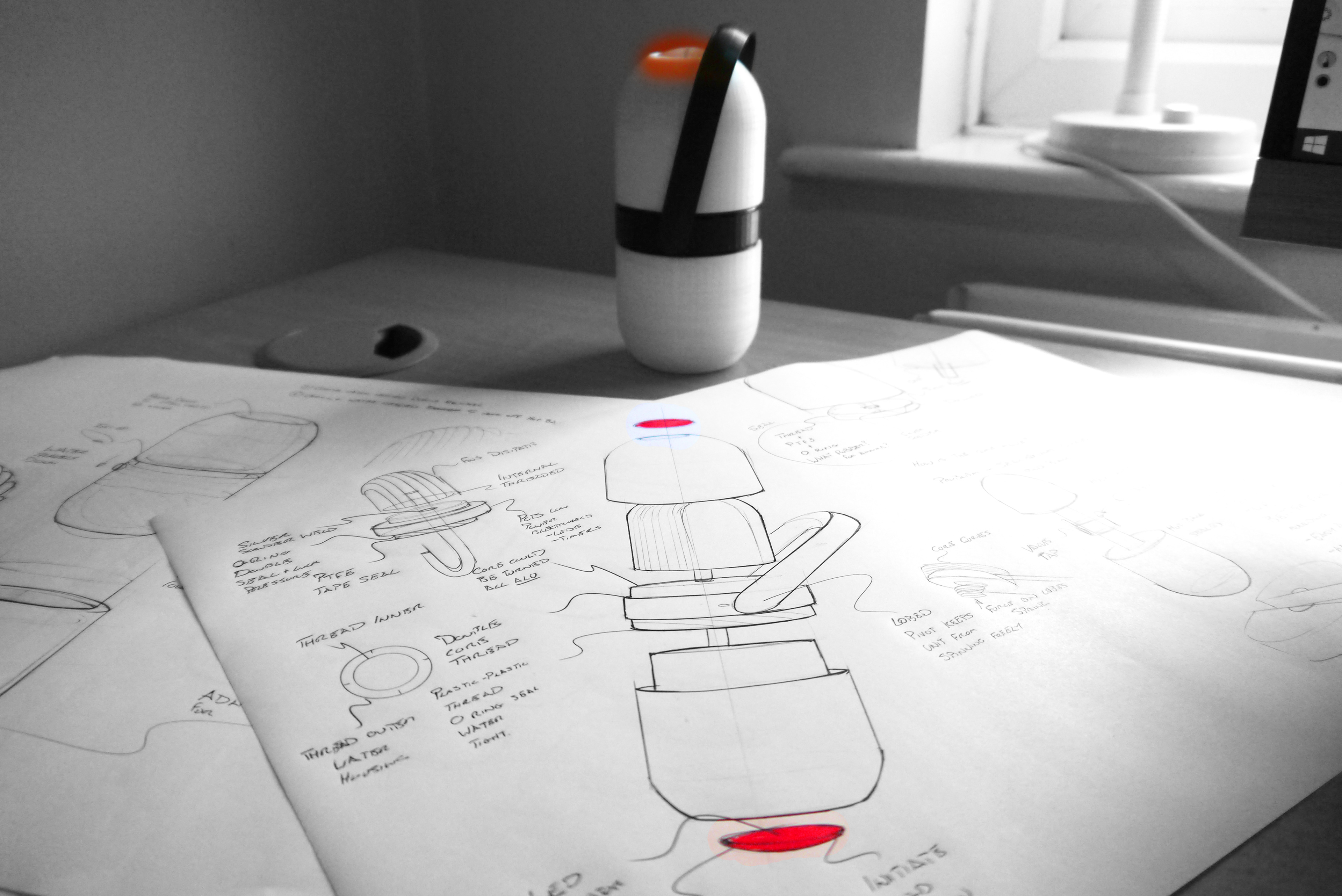
In order to make sure that Isobar was easy to use and not overly technical leading to failure to deliver vaccine due to user error, I conducted multiple user studies and ergonomic evaluations. I setup backpacks with weights, built simple electronic demonstrations and wrote a simple guidebook to simulate a nurse going through all the steps of retrieving vaccine and using the device. This led to multiple insights that went into developing 'ISO 1', the first complete physical prototype system.





Mechanical proof of principal
After designing a theoretical system, the next step was to prove that Isobar could achieve 10x cooling effect than competition. We developed our own insulation techniques and built pressure chambers and control circuits. On October 10 2017, ISO 2 achieved 88hrs of cooling @43 °C ambient environment with a device weighing under 8kg (the PATH small vaccine payload criteria).
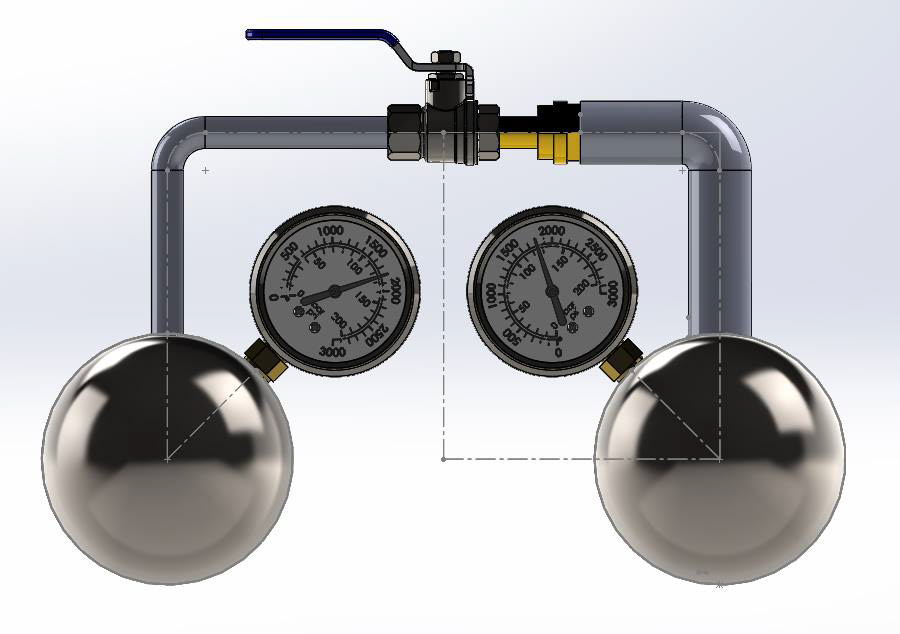
ISO2 Prototype model
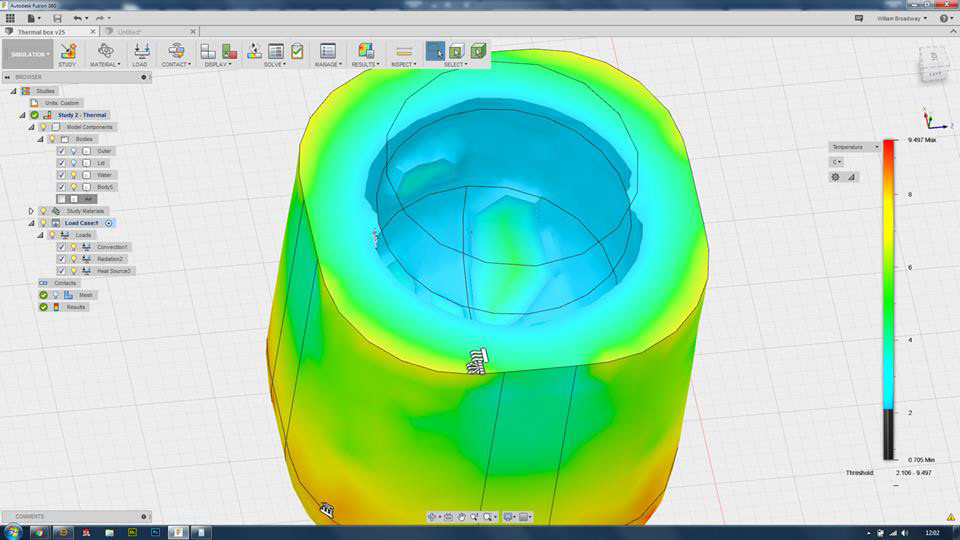
Thermal insulation optimization
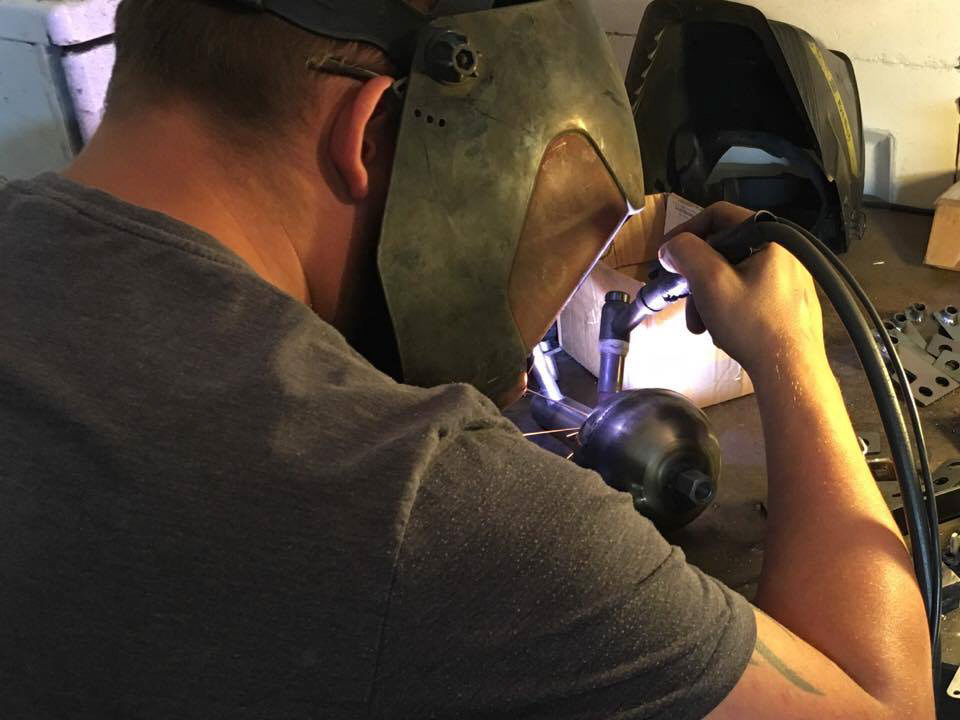

Silver solder welding
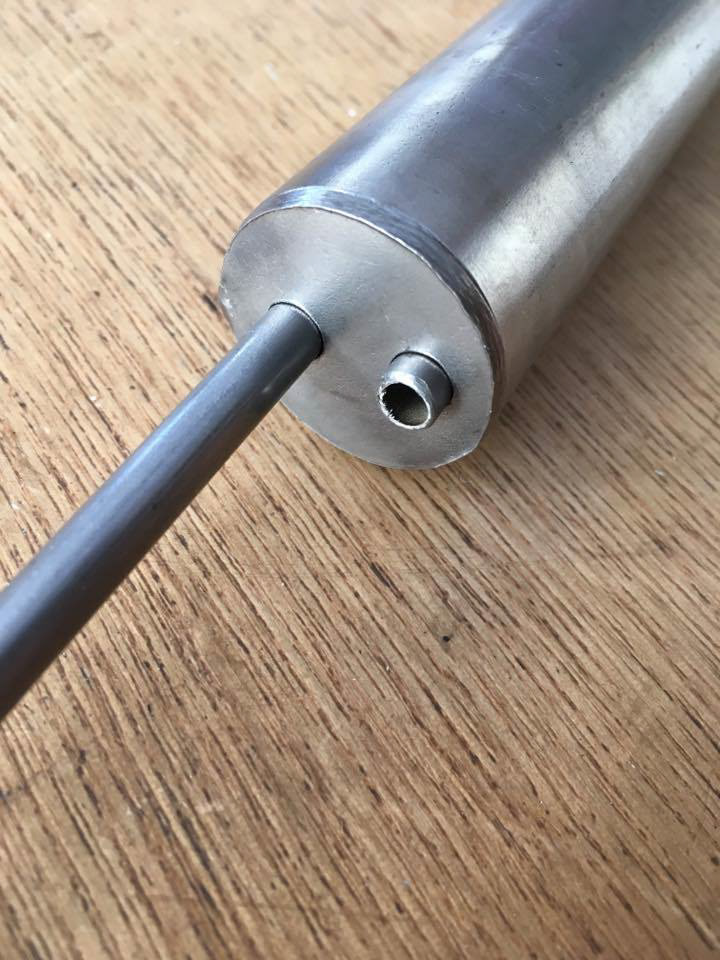

ISO2 Valve
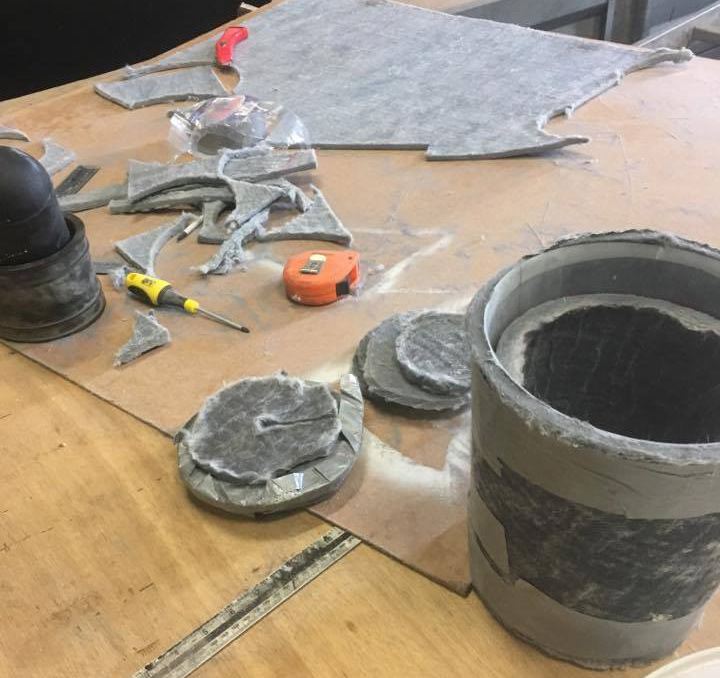

Creating advanced cooler box
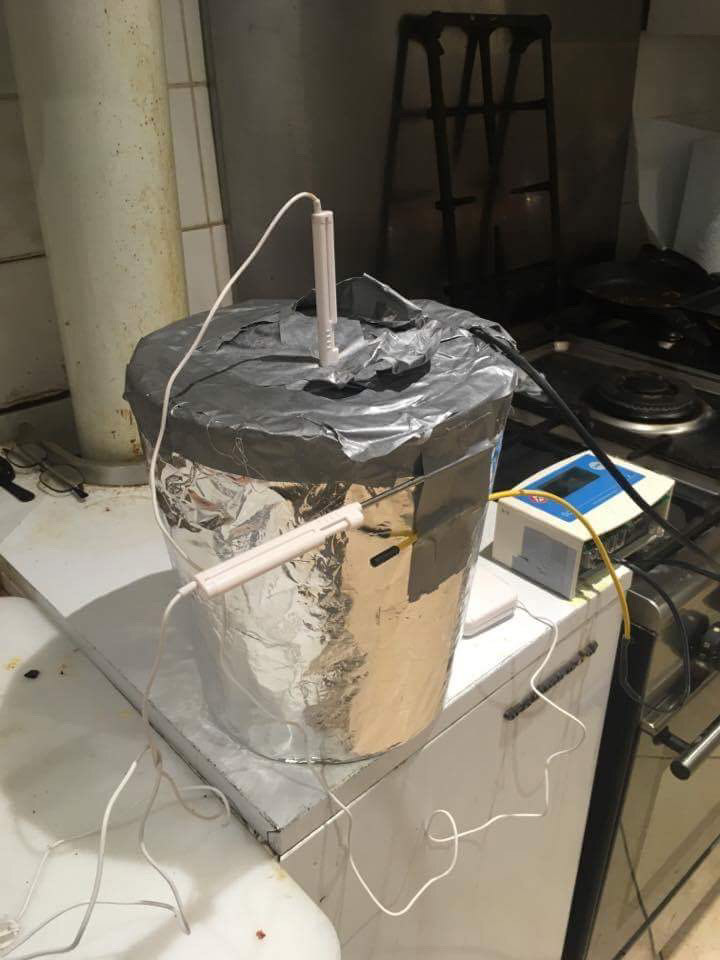

Testing container
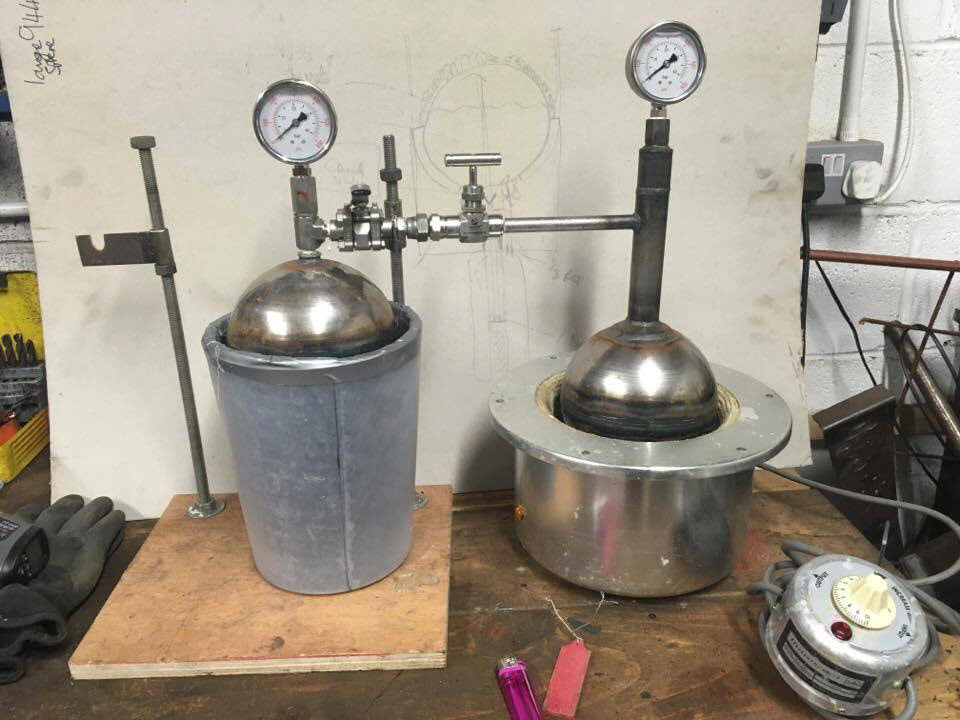

First working prototype
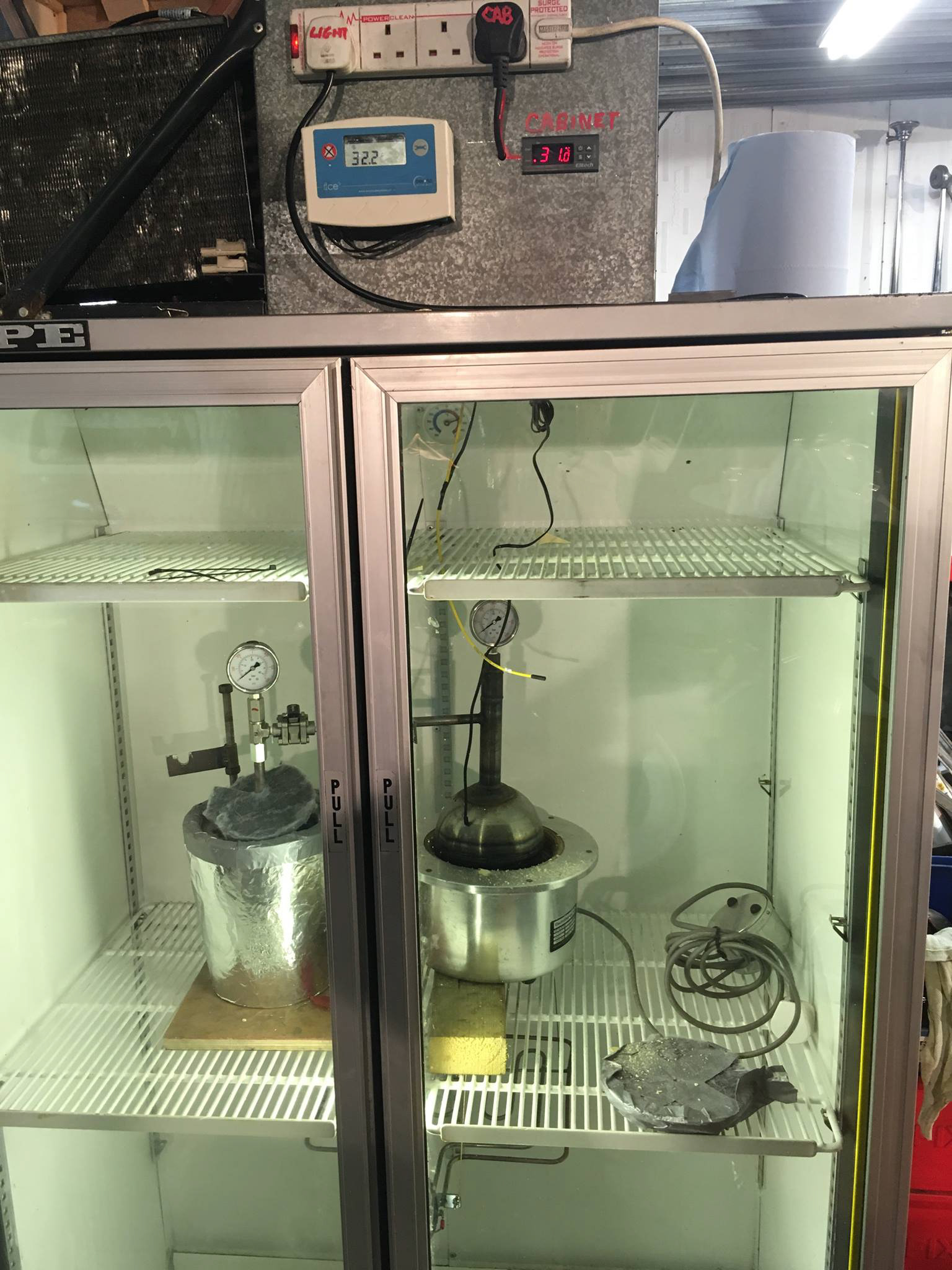

Testing in heated chamber
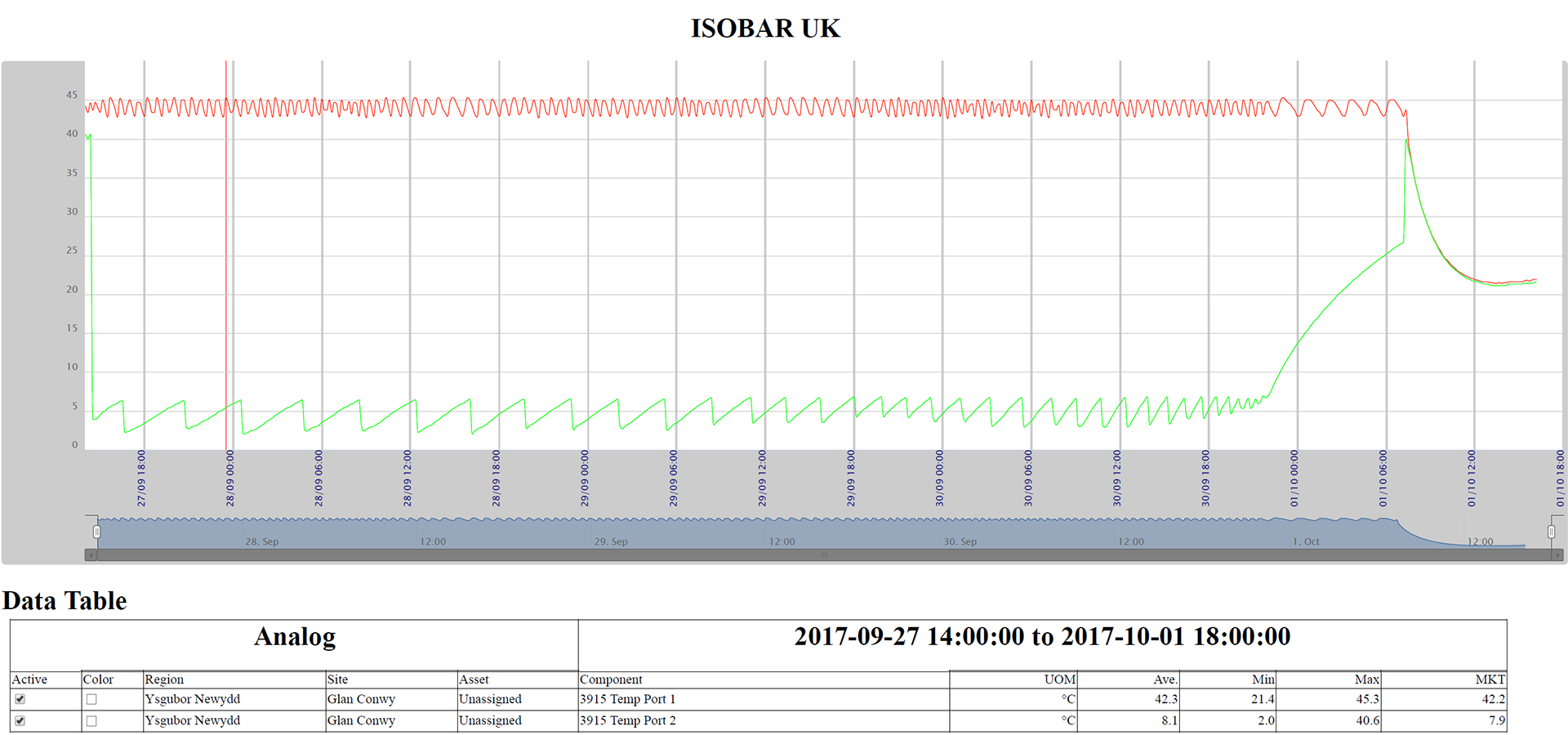
88hrs test @ 43°C

CAD ISO3
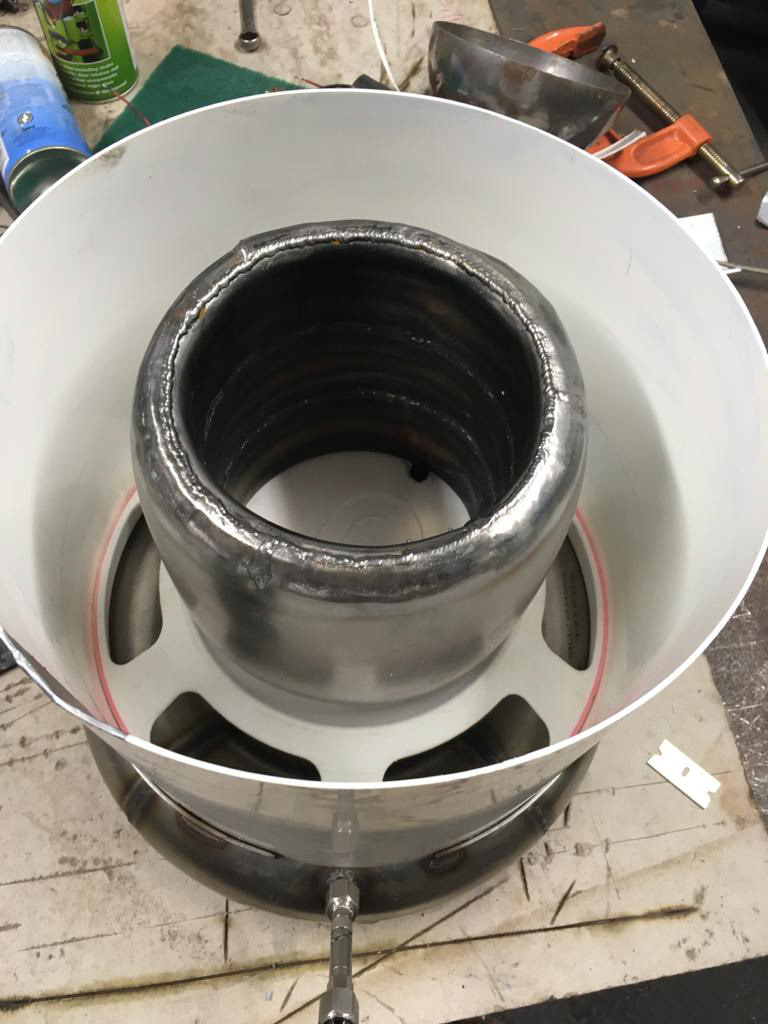

First toroidal tank
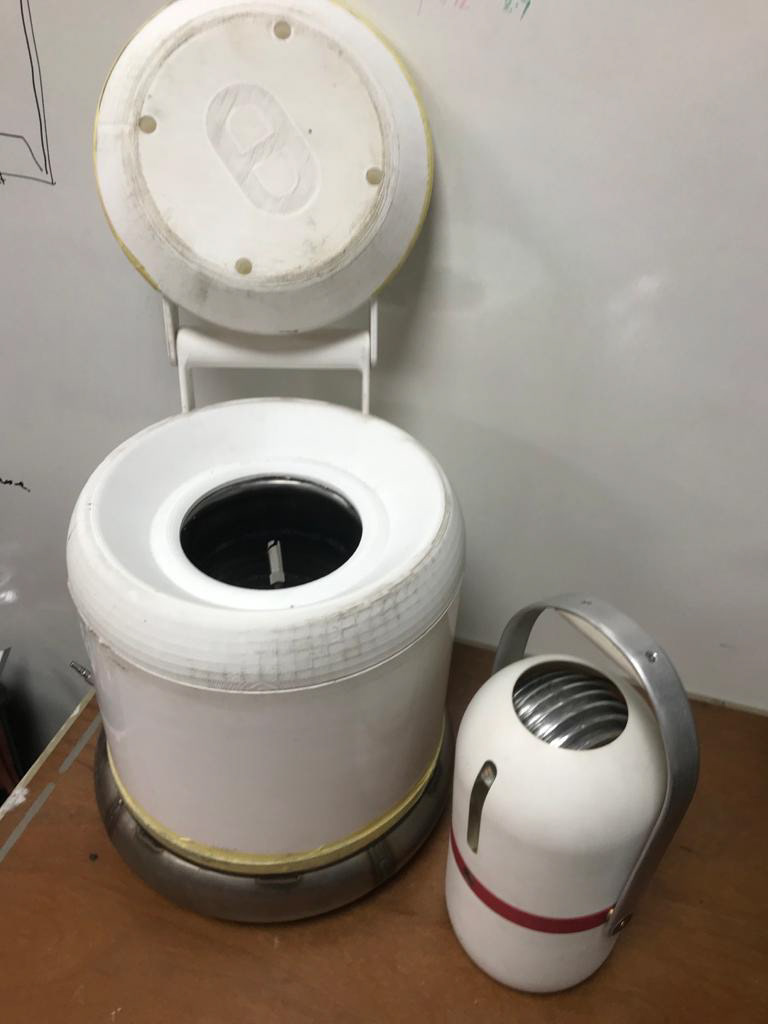

ISO 3 Prototype
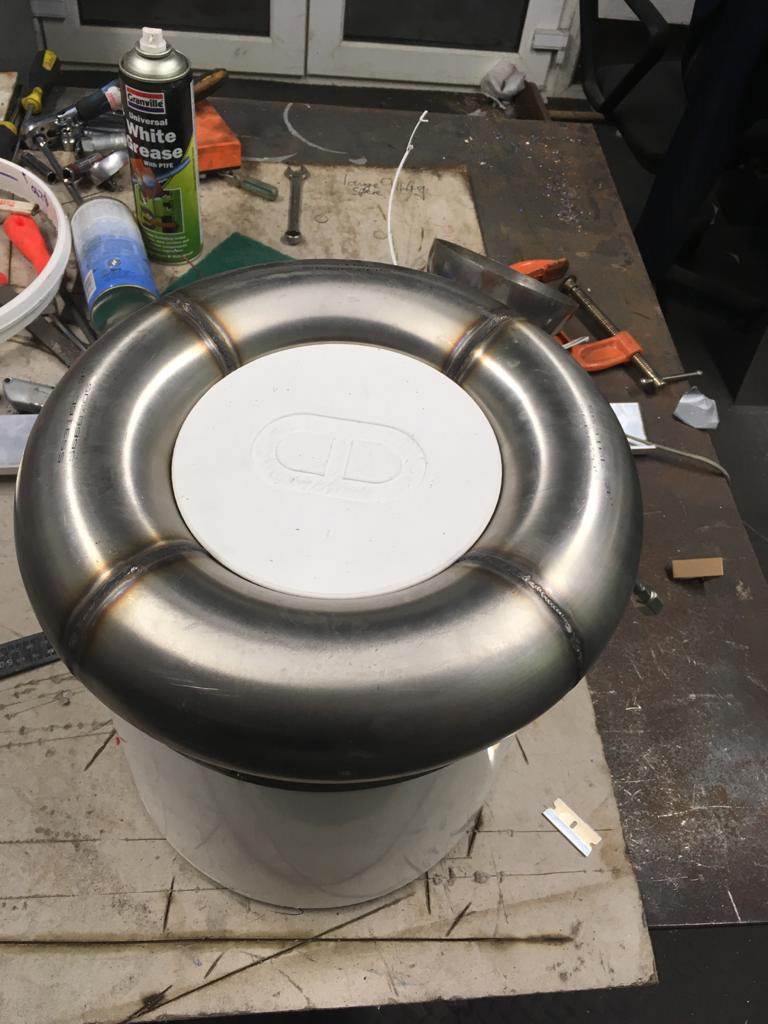

First lower toroidal tank
Future development
After the success of ISO 2 achieving 88hrs cool life at 43°C, development continued with ISO 3 &4, they feature an optimized design predicted to cool for around 120-180hrs from a single charge.
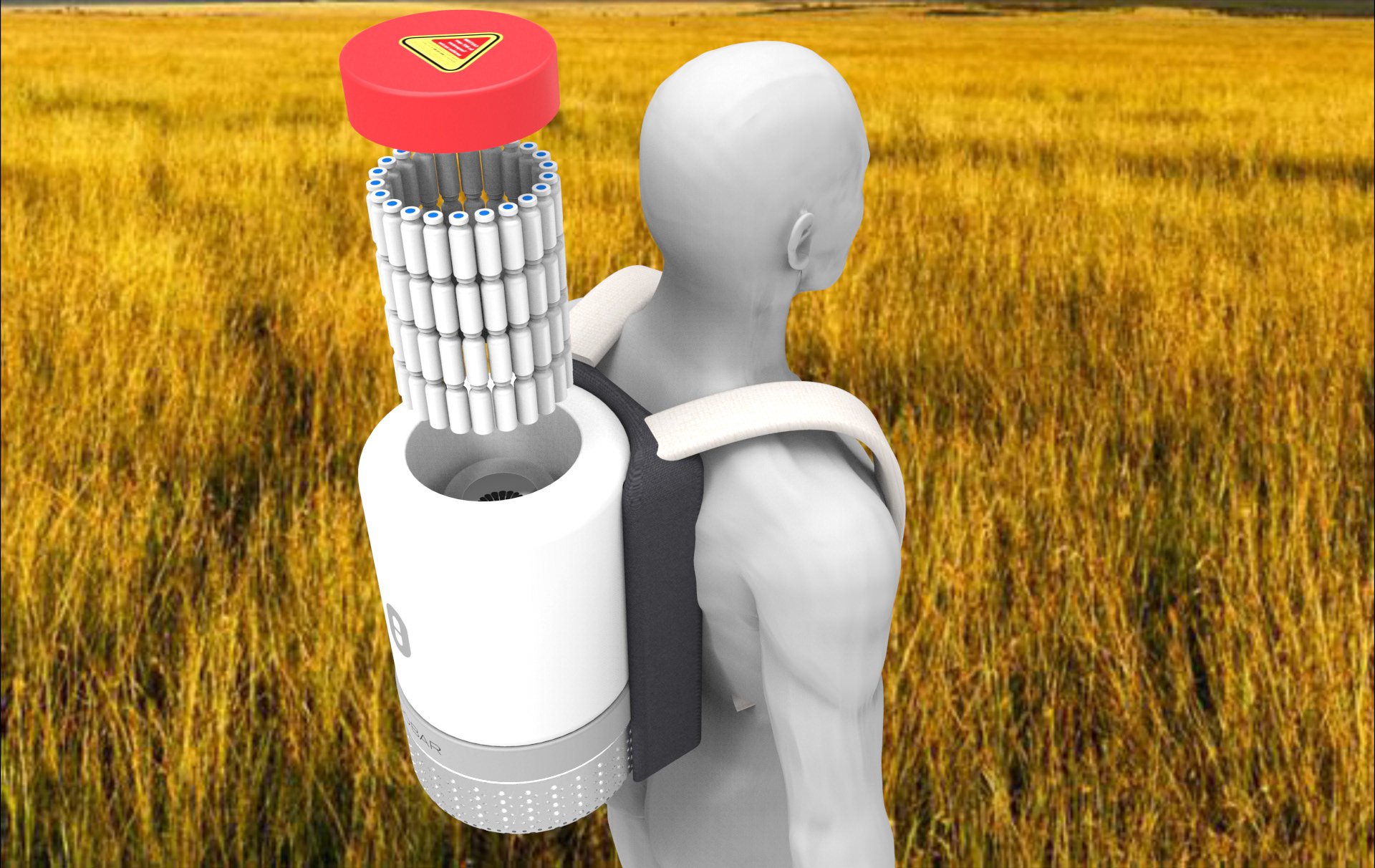
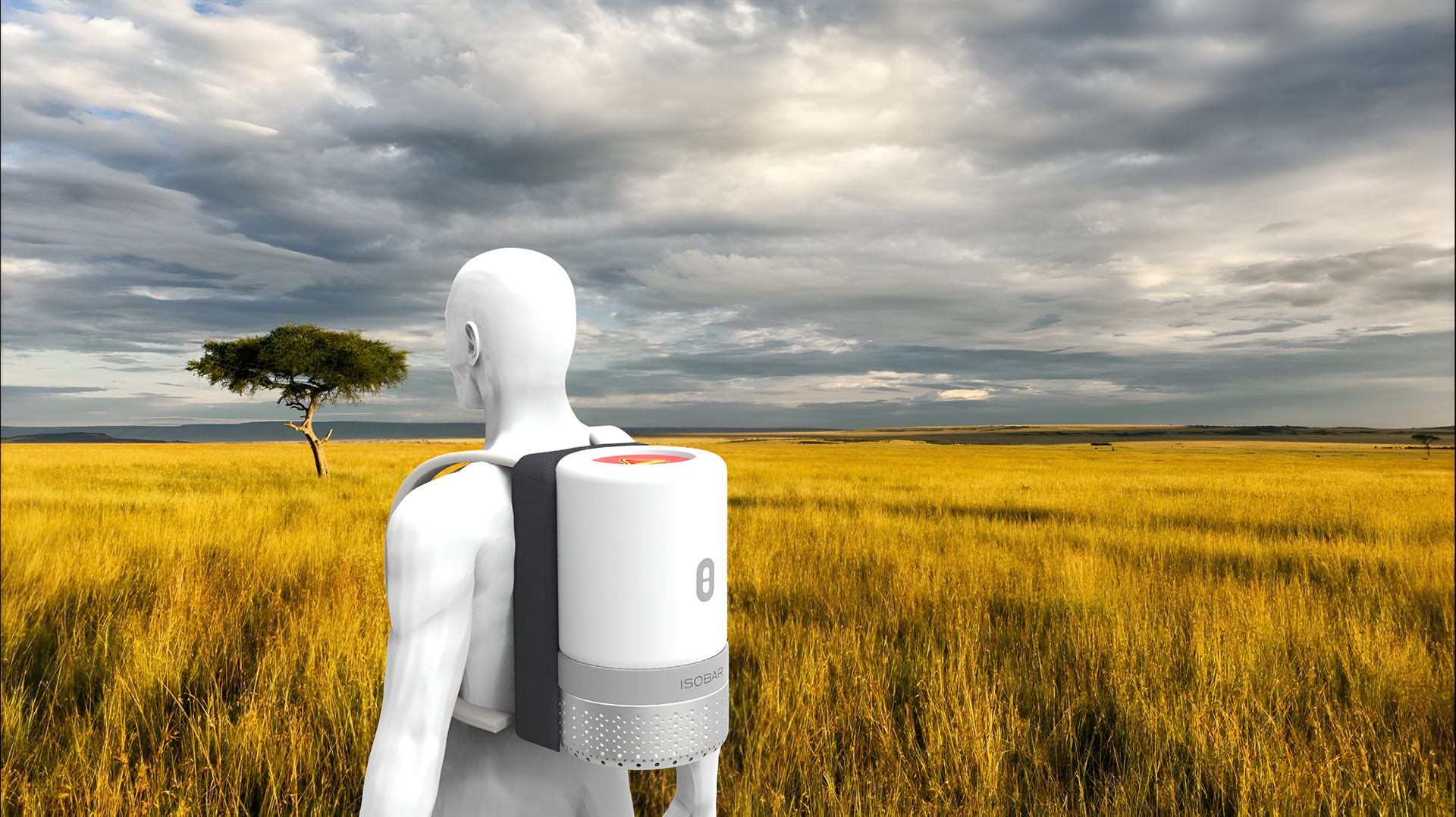


Awards and mentions
Bill Gates Tweet
The Guardian - Dyson Award Winner
Popular Science Article
BBC Newsbeat Article
McKinsey Venture Academy
National 2nd Place Morgan Innovation Prize
Runner Up Featured in National Science Museum London 2018


User research • Needs Testing • Cost analysis • Invention • Industrial Design • Mechanical Design • Design Validation • Business proposition